Are you tired of constantly struggling to keep your production line running smoothly? To overcome this you need to understand the 2 fundamental approaches to production management i.e. Push system vs Pull system.
In Lean manufacturing, push system vs pull system represent the contrasting philosophies that can significantly impact a company’s efficiency, inventory levels, and overall responsiveness to customer demand.
The choice between push system vs pull system is not just a matter of preference but a strategic decision that can make or break your Lean implementation.
I will discuss these concepts in detail along with their principles, benefits, challenges, and how to determine the best fit for your organization. Are you ready to master these two powerful approaches for driving Lean implementation? Then let’s get started…
Overview of Lean Manufacturing
Before getting into Push System vs Pull System differences, it is important to understand what is Lean Manufacturing. Lean Manufacturing is a methodology that focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity.
It is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement, involving everyone in the organization. It works on 5 principles of Lean i.e. Value, Value Stream, Flow, Pull, and Perfection.
The primary objective is to create more value for customers with fewer resources. You know WASTE is any activity that does not add value from the customer’s perspective.
By focusing on waste reduction Lean Manufacturing helps companies improve quality, reduce lead times, and lower costs. At the heart of Lean are various systems designed to streamline production processes, among which are the fundamental push system vs pull systems.
These systems dictate how work is scheduled and resources are utilized, impacting everything from inventory levels to customer satisfaction. These systems represent the 2 distinct categories for managing the flow of materials and products through production.
Understanding the Push vs Pull system is important for optimizing production and Lean objectives. Let’s understand both types of systems one by one and then I will compare them based on different parameters.
What is a Push System?
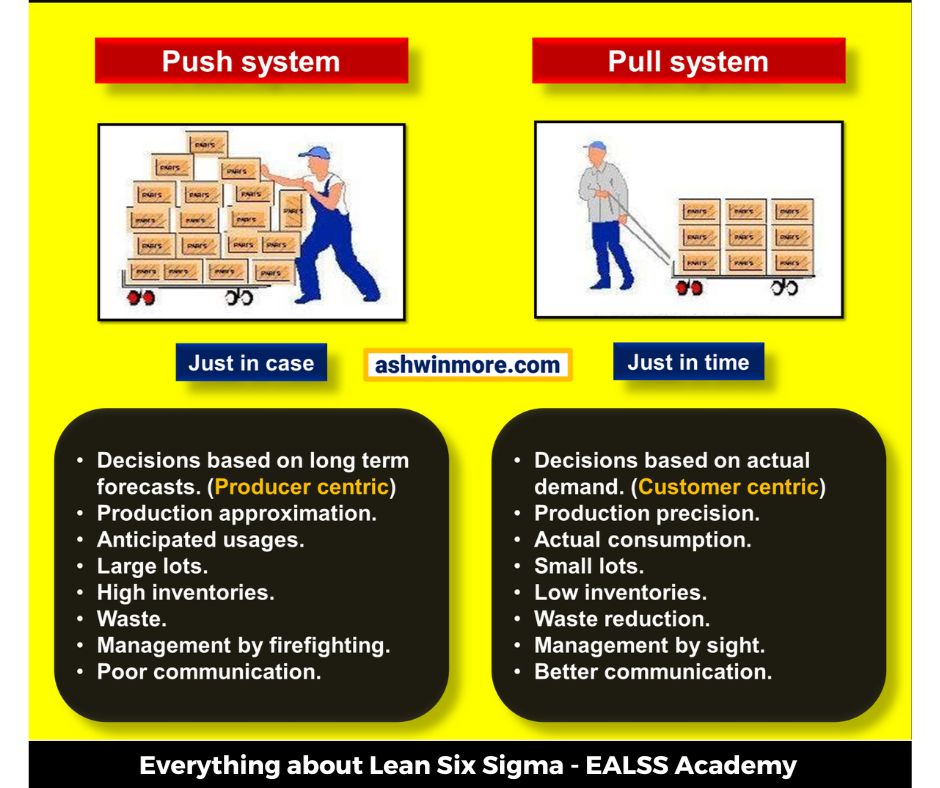
The 1st type i.e. Push system is a production strategy where the flow of goods and materials is determined by forecasted demand rather than actual customer orders.
In this system, production schedules are created based on predictions of future demand, and goods are pushed through the production process to build inventory in anticipation of sales.
The primary goal is to ensure that products are readily available to meet customer demand as they arise. This system operates on a principle of proactive production driven by forecasts and planning.
How does the Push system work?
- Forecasting demand: The process begins with analyzing market trends, historical data, and sales projections to forecast future demand for products. This forecast guides the entire production plan.
- Production planning: Based on demand forecasts, production schedules are developed. These schedules dictate the quantity of each product to be manufactured within a specific time. It also includes procurement of raw materials and components needed.
- Material requisition and inventory: Once the production plan is set raw materials and components are ordered from suppliers. These materials are then stored in inventory, ready to be used in the production process.
- Manufacturing process: Production begins according to the established schedule with goods being produced and assembled based on the forecasted demand. Here emphasis is on keeping the production line moving to meet the planned output.
- Inventory Accumulation: As products are manufactured they are stored as finished goods inventory. This inventory acts as a buffer ensuring that products are available for immediate shipment when customer orders are received.
- Distribution and sales: The finished goods are then distributed to various warehouses, retailers, or directly to customers. The push system aims to have sufficient stock on hand to fulfill customer’s orders without delay.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
- A push system can lead to high production volumes because it focuses on producing goods based on forecasted demand. This is effective for companies with stable demand patterns.
- By producing large quantities, companies can take advantage of economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit. This is particularly beneficial when production processes have high fixed costs.
- The system maintains a buffer stock, which can be useful in preventing stockouts and ensuring that products are readily available for customers, even if there are fluctuations in demand.
- Production schedules are more predictable as they are based on forecasts rather than actual demand. This can simplify planning and resource allocation.
- This system helps in maximizing the utilization of production capacity by keeping machines and workers busy, which can reduce downtime and increase efficiency.
Disadvantages:
- The most complicated risk in the push system is overproduction. Producing more than the actual demand can lead to excess inventory, increased holding costs, and potential waste.
- The push system relies on demand forecasts which can be inaccurate sometimes. Inaccurate forecasts can lead to either overproduction or underproduction causing stockouts or excessive inventory.
- Maintaining large inventories requires significant storage space and capital investment. It also involves additional costs, such as insurance, handling, and potential obsolescence.
- The push system is less responsive to changes in demand. It can be challenging to adjust production schedules quickly, leading to inefficiencies and potential customer dissatisfaction.
- Managing a push system can be complex as it involves coordinating multiple stages of production and inventory management. Any disruption in the supply chain can have negative effects leading to delays and inefficiencies.
What is a Pull System?
The 2nd type of system is the pull system where production is driven by actual customer demand rather than forecasted demand or a predetermined schedule. It is more reactive and adaptive, ensuring that production aligns closely with customer needs.
This system is based on the principle that materials and products should only be produced and moved when there is a need or demand for them. It ensures that each step in the production process only takes place when the next step or customer signals a need.
Before comparing the Push system vs the Pull system you need to know that this system operates on the concept of Just In Time (JIT) Production, where products and materials are only produced and delivered as needed.
How does the Pull system work?
- Customer demand signals: The pull system starts with the end customer. When a customer places an order, this creates a demand signal.
- This signal is transmitted backward through the production process to trigger the creation of necessary components and assembly of the final product.
- Kanban system: This involves visual signals such as cards, or electronic alerts. These signals indicate when more materials or products are needed at each stage of production. Kanban card acts as a signal between different workstations.
- Controlled inventory levels: In the pull system, inventory levels are tightly controlled. Rather than stockpiling large quantities of materials or finished goods, companies maintain minimal inventory levels called buffer stock.
- This approach reduces waste and storage costs and ensures that production is closely aligned with actual customer demand.
- Continuous flow: The goal of the pull system is to create a smooth continuous flow of material and products through the production process. By responding directly to customer demand, the system minimizes delays and reduces lead times.
- Flexibility and responsiveness: Production is based on real-time demand, companies can quickly adjust to changes in customer preferences, market conditions, or supply chain disruptions.
- This flexibility and responsiveness help companies avoid excess inventory and meet customer needs more effectively.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
- The pull system operates on actual customer demand, which minimizes production so that companies can maintain lower inventory levels which ultimately reduces storage cost and inventory waste.
- By producing goods using the JIT approach, the pull system streamlines production processes. This leads to fewer bottlenecks, reduced lead times, operational cost reduction, and improved overall efficiency.
- Pull systems are highly responsive to changes in customer demand. They allow manufacturers to quickly adjust production schedules, product types, and quantities enhancing flexibility and responsiveness.
- As we know the pull system encourages smaller batch sizes, and there is more frequent inspection and quality control. This often leads to higher product quality and quicker detection of defects.
- By closely aligning production with customer demand, companies can provide more accurate delivery times and maintain better product availability, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages:
- Pull system requires reliable suppliers who can deliver materials on time. Any delays or inconsistencies from suppliers can disrupt the production process and lead to shortages.
- The JIT approach sometimes can create pressure on the workforce to meet production demand quickly and accurately. This can lead to stress and potential burnout if not managed properly.
- Pull systems are highly dependent on accurate demand forecasting. Sudden spikes or drops in demand can cause production issues, either leading to shortage or excess inventory.
- With reduced inventory levels in the pull system, there is a risk of stockouts if demand is higher than anticipated or if there are disruptions in the supply chain.
Differences: Push System vs Pull System
Till now I discussed the fundamentals of the push and pull system along with their advantages and disadvantages. Now let’s understand the Push system vs Pull system differences by considering all the important parameters.
| Parameter | Push System | Pull System |
| Definition | Production is based on forecasted demand and schedules. | Production is based on actual customer demand. |
| Production Trigger | Initiated by predictions and proper planning. | Initiated by real-time demand signals such as Kanban card. |
| Inventory Levels | Higher inventory level – stocks are kept to meet forecasted demand. | Lower inventory level – inventory is minimized to what is needed for current orders. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, difficult to adjust to changes in demand. | More flexible, can quickly adapt to changes in demand. |
| Lead Time | Often longer due to excess inventory and production planning. | Usually short, as production aligns closely with demand. |
| Waste | Higher risk of overproduction, excess inventory, and obsolescence. | Reduced waste, as production is more closely matched to demand. |
| Production efficiency | Can be inefficient due to potential overproduction and waiting | More efficient, as it reduces waiting time and aligns production with actual demand. |
| Customer focus | Less responsive to actual customer needs, more focus on internal efficiencies | Highly responsive to customer needs, the focus is on fulfilling real-time orders. |
| Forecast Accuracy | Critical: inaccuracies can lead to overproduction or stockouts. | Less dependent on forecasts: production is based on actual orders. |
| Control System | Centralized control: decisions are made based on planning and forecasting. | Decentralized control: decisions are made based on real-time data and signals. |
| Implementation Complexity | Easier to implement but harder to optimize due to variability in forecasts. | Requires a well-coordinated system and may involve more complex logistics. |
| Practical Application | Often used in industries with stable and predictable demand like the Automobile industry. | Ideal for environments where demand is volatile or products are customized like E-commerce |
| Example | Traditional manufacturing, where goods are produced in large batches. | Just In Time (JIT) systems, where production is triggered by customer orders. |
Practical solution to overcome challenges in Push vs Pull system
Now you know the push system vs pull system differences, the next important point is how to overcome challenges while implementing both systems in your company. Let’s understand that…
Demand variability:
You can use demand smoothing techniques like demand leveling and buffer stock to manage fluctuation in demand. This can help in both push and pull systems by smoothing out the peaks and downs in production schedules.
Use data-driven forecasting to leverage historical data, market trends, and advanced analytics to improve demand forecasting accuracy in the push system. For the pull system, maintain a close relationship with customers to receive timely demand signals.
Communication and coordination:
Establish clear standardized communication protocols across the supply chain. For that you can use digital tools like real-time data sharing and decision making.
Create cross-functional teams involving sales, production, and supply chain personnel to ensure alignment and quick decision-making.
Inventory management:
In the push system, implement practices like Just In Time (JIT) and Kanban to reduce inventory levels. In the pull system, use visual management tools to monitor inventory levels and trigger replenishment only when needed.
For both systems, consider Vendor Managed Inventory arrangements where suppliers manage inventory levels based on real-time data, reducing the burden on the company.
Lead time management:
Identify and eliminate bottlenecks in the production process to reduce lead times. Use techniques like Value stream mapping to streamline processes and remove non-value-added activities.
Invest in flexible manufacturing systems that can quickly switch between products, enabling faster response to changes in demand in the pull system.
Now you understand the Push system vs Pull system differences and ways to overcome the challenges during their implementation. But you know we discussed the theory part you will understand its implementation when you learn this under the guidance of an expert.
For that, I would recommend you to join EALSS Academy’s Lean Expert with 38 Lean Tools live training and 3 certification programs to learn the Push and Pull system with practical examples under the guidance of Lean specialists.
Just click on the above link register for the program and join the official group of EALSS Academy. You can watch 1hrs FREE session recording inside to understand the instructor’s teaching style.
Their support team will provide you with complete details about how to enroll in this program and get certified in 3 levels of Lean. (Check out – All You Need to know about Lean Expert Live training program)
Conclusion
Understanding the push system vs pull system differences is crucial for optimizing efficiency and responsiveness within your production processes. Selecting the system is based on the specific needs and dynamics of your production environment.
The push system is highly effective in an environment where demand is predictable and stable. On the other hand, the pull system is driven by actual demand and offers a more flexible and responsive approach, producing things only what is needed and when it is required.
Instead of choosing between the push system vs pull system you can think of a hybrid approach and leverage the strength of both systems. Use a push system for stable and high-volume products and a pull system for more volatile, low-volume items.
If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to get more such articles every week.






Pull System tiene muchas ventajas comparada con Push System y con los modelo de gestión de demanda basadas en Forecast
Como consultor en Lean Sigma yo he implementado y aplicado Pull System y hemos logrado mejorar el nivel de servicio (disminución de agotados a menos de la mitas )y disminución de inventarios en más del 30%
La clave del éxito en este sistema radica en varios aspectos como
– Deseñar el modelo con las restricciones propias de la empresa: Lead Time de los proveedores, OEE de la planta, Tiempos de alistamiento entre otras variables
– Acompañar la implementación del Pull System con una aplicación de SMED en las lineas de producción
– S&OP bien aplicado para mantener el flujo de información desde y hacia el comercial – operaciones
Actualmente estoy desarrollando una APP con el fin de que las empresas puedan usar, tanto para la compra de materias como para la planeación de sus productos aplicando Pull System.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts!