Have you ever wondered why some projects or processes fail despite proper planning and execution? The answer lies in understanding and mitigating potential failures before they occur. This is where FMEA comes into play.
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach that empowers teams to anticipate and address potential failures before they occur. This is one of the powerful tools from the Lean Six Sigma practitioners toolkit.
By systematically identifying failure modes, assessing their potential effects, and implementing proactive measures FMEA enables organizations to safeguard their processes and products against costly defects and downtime.
In this article, I will discuss this powerful tool in detail along with its benefits, core concepts, and importance, and walk you through the step-by-step process of conducting a Failure Mode Effect Analysis.
Are you ready to identify potential failure modes in your processes? Then let’s get started…
What is FMEA?
Failure mode effect analysis is one of the powerful tools used in Lean Six Sigma methodology to identify potential failures in a process, product, or service and to prioritize actions to mitigate or eliminate these failures.
It’s like proactive detective work where you need to anticipate possible causes before they occur rather than reacting to them after the fact. You can also call this a structured approach to understanding and managing the risks.
It involves systematically analyzing every component of a process or system to identify potential failure modes means different ways in which the process or system could fail.
Also involves assessing the severity of the impact, if that failure were to occur, determining the likelihood of the failure happening, and evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls to prevent or detect the failure.
This analysis results in a prioritized list of actions to address the most critical failure modes in the process or system. Ultimately ensure the delivery of high-quality products and services to customers while minimizing risks and costs.

Let’s understand with a simple example, suppose you are manufacturing a car. FMEA would involve breaking down the car into its components like the engine, brakes, electrical system, etc.
Identifying potential ways each component of the car could fail like engine overheating, brake failure, or electrical short circuit, and then assessing the consequences of each failure like engine failure could lead to a breakdown, brake failure could result in an accident, etc.
So by systematically going through this process of analysis, you can anticipate and prevent problems before they happen. That’s why it is called a proactive approach to defect prevention.
If you see the history of this powerful tool you will understand that this tool originated in the 1940s within the aerospace industry, particularly during World War II as a method to identify and address potential failure modes in military equipment.
Over time FMEA has evolved and found applications in different industries like automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and software development.
Today, it is considered one of the important tools in quality management systems and is also integrated with continuous improvement methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma.
Basically, FMEA plays an important role in quality management by helping organizations proactively identify and address potential sources of defects, errors, or inefficiencies.
By systematically analyzing risks and implementing appropriate controls, organizations can reduce the likelihood of failures occurring, improve product or service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately increase profitability.
It is like preventive medicine for processes or systems, helping organizations stay ahead of potential problems, and continuously improve their performance. By integrating it into QMS, organizations can become agile, and competitive in the market.
Types of FMEA
There are 3 important types of failure mode effect analysis and each type serves a unique purpose in ensuring the quality and reliability of products and processes. Let’s see these 3 types one by one:
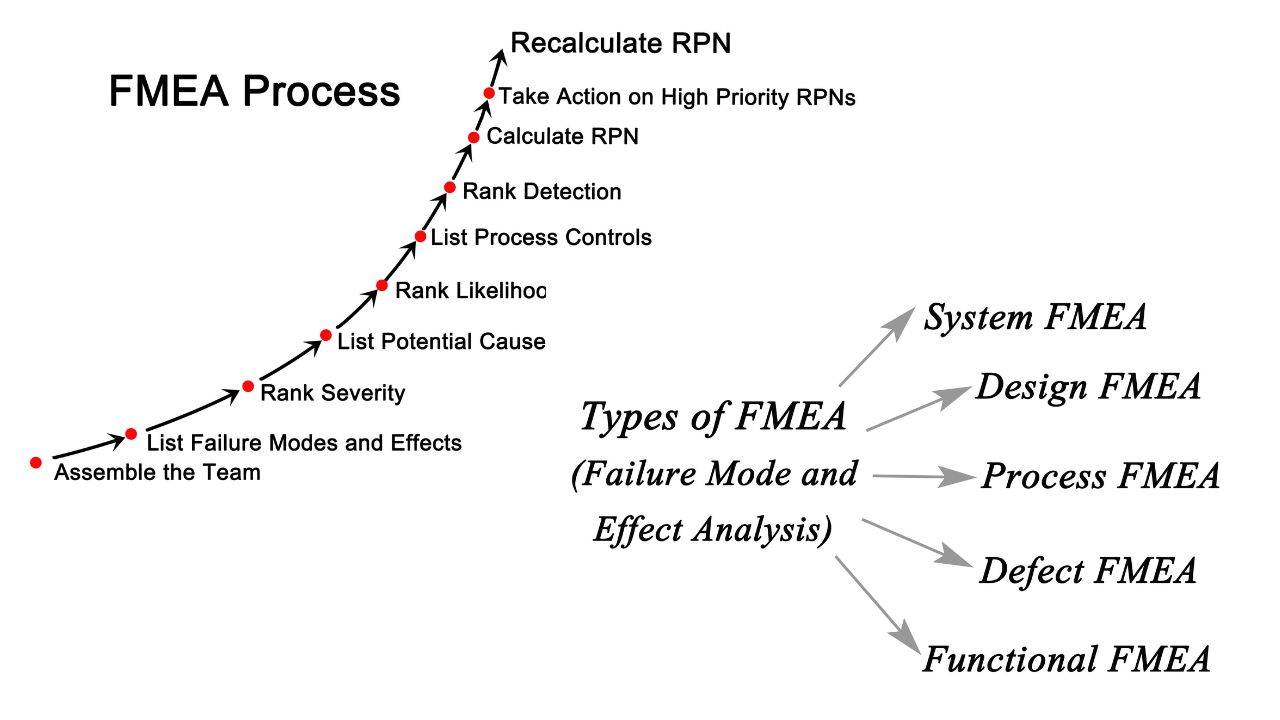
1. System FMEA:
- SFMEA type focuses on analyzing failures that can occur at the system level. It is used primarily during the design phase of a product or process.
- It examines how different components or subsystems interact with each other and identifies potential failure modes that could arise from these interactions.
- For example, in the design of a new automobile system, FMEA would identify potential failures related to the engine, transmission, braking system, etc., and asses their potential effects on the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
2. Design FMEA:
- DFMEA is more specific and focuses on analyzing potential failures associated with the design of individual components or subsystems within a system.
- It is conducted during the product development phases to ensure that potential failures are identified and addressed before production begins.
- It helps design engineers understand how different design parameters and specifications could lead to failures and their effects on the overall functionality and reliability of the product.
- For example, in the design of a smartphone DFMEA would assess potential failures related to the screen, battery, circuitry, etc., and their impact on use experience and product performance.
3. Process FMEA:
- PFMEA shifts the focus to the manufacturing or operational phase of a product or process. It examines potential failures that could occur during the manufacturing or assembly process and their effects on product quality and performance.
- This helps identify weaknesses in the production process such as machine malfunctions, human errors, material defects, etc., and allows organizations to implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of these failures occurring.
- For example, in the production of electronic components, PFMEA would assess potential failures related to soldering, component placement, testing procedures, etc., and their impact on product reliability and performance.
4. Defect FMEA:
- It is used to identify and prioritize potential defects or failures in a product, process, or service. It helps you anticipate problems that might arise in whatever you are working on, whether it’s making a product, delivering a service, or carrying out a process.
- It is like detective work done in advance to figure out where things could go wrong and what could happen if they do. Using this you can brainstorm all the possible ways something could fail.
- For example, if you are making a car, failure modes in the context of defects could include engine malfunctions, brake failures, oil leakage, paint defects, etc.
5. Functional FMEA:
- Unlike traditional FMEA, which focuses on failure modes and their effects on components, functional FMEA zeroes in on the functions or intended purposes of these components.
- Start with clearly defining the functions of the system, process, or product under analysis. Functions represent what the system is supposed to do or achieve.
- For example – If you are analyzing a car’s braking system, functions would include decelerating the vehicle safely and maintaining control during braking.
- Once the functions are identified, you can brainstorm potential failure modes with your team that could prevent those functions from being fulfilled.
When to use Failure Mode Effect Analysis?
Failure mode effect analysis helps you identify potential breakdowns in processes, products, or systems before they happen. Let’s see some of the conditions where you can use this powerful tool:
- New Product or Process Development: When you are creating something new like developing a new product or designing a new process, failure mode effect analysis can foresee potential issues.
- Let’s say you are designing a new smartphone, this tool can help you pinpoint where the phone might fail like the battery draining too quickly or the screen cracking easily.
- Process improvement: If you are trying to improve an existing process, this tool can highlight areas for enhancement or areas where you can make improvements.
- For example, if you run a manufacturing plant and want to reduce defects in your products, FMEA can reveal weak spots in the production line where defects are likely to occur.
- Risk management: This tool is effective for risk management as well. It allows you to assess the severity, occurrence, and detectability of potential failures. This helps prioritize which issues need immediate attention.
- Let’s say you are a hospital administrator, this tool can help you anticipate potential risks in patient care processes like medication errors or surgical complications.
- Compliance requirements: In industries with strict regulations like aerospace or healthcare using Failure mode effect analysis is mandatory.
- It demonstrates that you have thoroughly analyzed potential risks and taken steps to mitigate them. This can help ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Continuous improvement: Even after implementing changes to address identified risks you should periodically revisit and update your FMEA to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
- This keeps you proactive in identifying and addressing potential failures. Ultimately this is a continuous improvement tool.
How to perform FMEA?
Let’s discuss the simple steps to perform Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) to proactively identify and mitigate potential failures in your processes, products, or systems that ultimately improve overall quality and customer satisfaction.
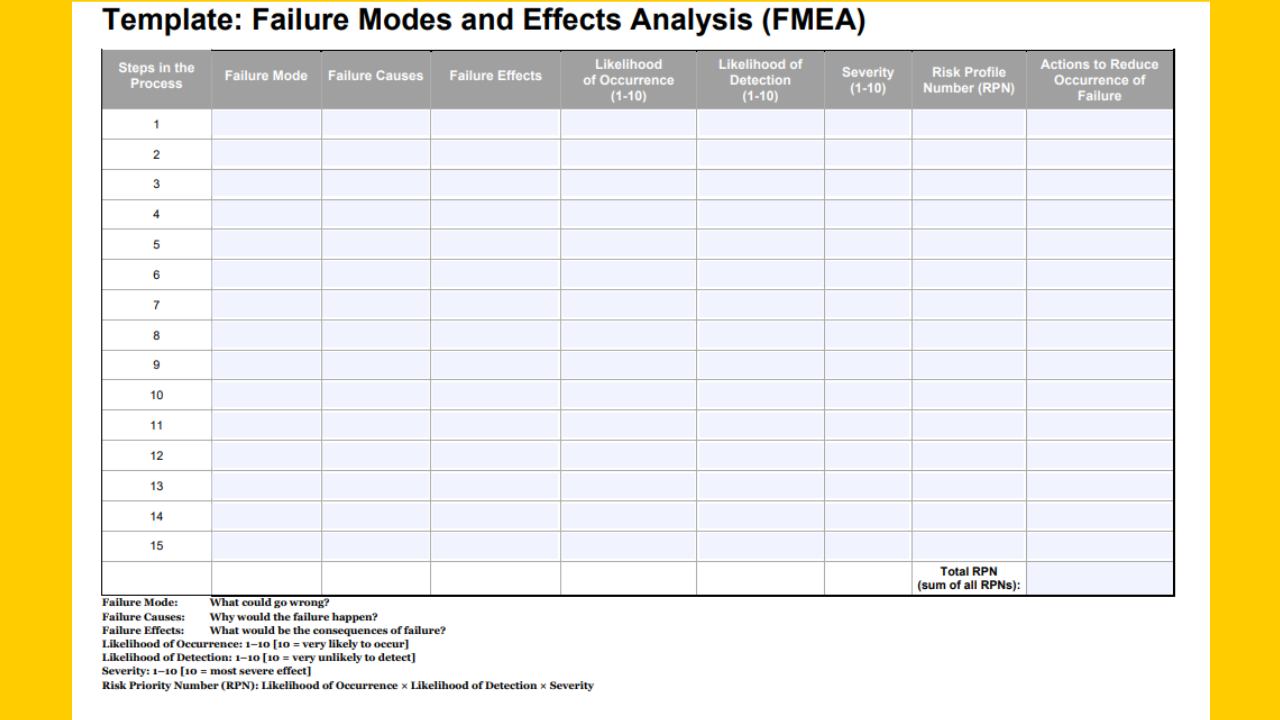
1. Select the process/product/system:
Determine the specific process, product, or system you want to analyze. That could be a manufacturing process, product design, service delivery process, or any process within your organization. Select and evaluate this properly.
2. Assemble the Team for analysis:
You need cross-functional teams that include Subject matter experts and people with knowledge and expertise relevant to the process, product, or system being analyzed.
This includes people from different departments like engineers, designers, quality assurance professionals, operators, supervisors, process owners, etc.
3. Define the Scope and objectives:
Clearly define the scope of analysis by discussing it with the team. What are the boundaries of the process or system you are analyzing? What specific aspects like functions, components, or process steps will you focus on?
4. Identify Potential Failure Modes:
Brainstorm and list all the possible failure modes that could occur within the defined scope. Failure mode is a specific way in which a process, product, service, or system could fail to meet its intended function or requirements.
Use techniques like process mapping, historical data analysis, and input from team members to identify potential failure modes. Encourage team members to think creatively and consider past similar situations.
5. Identify root causes of failures:
Determine the root causes or factors contributing to each failure mode. Why might this failure occur? What are the underlying reasons behind each failure mode?
You can use tools like cause and effect diagrams, 5 Whys analysis, and historical data analysis to uncover the underlying causes of the potential failure mode.
6. Determine the effects of failure:
For each identified potential failure mode, determine the potential effects or consequences it could have on the process, product, system, or service.
Consider the impact on safety, quality, performance, reliability, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. Think from all sides.
7. Assign the occurrence ratings:
Estimate the likelihood or frequency of each failure mode occurring. Assign an occurrence rating to each failure mode based on historical data, expert judgment, and process knowledge.
Use a predetermined scale (1 to 10), where 1 means low occurrence rates and 10 means higher occurrence rates.
8. Assign the detection ratings:
Evaluate the effectiveness of current controls or detection methods in detecting each failure mode before it reaches the customer or causes harm. Assign a detection rating to each failure mode using a scale of 1 to 10.
This rating indicates the likelihood of detection. 1 means a lower rating that implies a higher likelihood of detection and 10 means a higher rating that implies a lower likelihood of detection.
9. Assign the Severity ratings:
Assign the severity rating to each potential effect to quantify the seriousness of its impact. While rating considers factors like safety, compliance, customer impact, and financial consequences.
You need to evaluate the potential impact of each failure mode on the overall process, product, service, or system.
Here also use a scale (1 to 10) for severity rating, 1 means low severe consequences on the process or product and 10 means higher severe consequences of the process or product.
10. Calculate Risk Proioty Number (RPN):
At this step, calculate the RPN number for each failure mode by multiplying their severity, occurrence, and detection ratings together (RPN = S×O×D).
RPN number provides a numerical value that represents the overall risk associated with each failure mode. This helps prioritize which failure modes to address first. Focus on High RPN items for mitigation.
11. Prioritize actions to deal with failure modes:
Prioritize the failure modes with the highest RPNs for corrective action. These are the failure modes with the highest potential impact and likelihood of occurrence combined with poor detection.
Prioritize actions to address high-risk failure modes by focusing on those with the highest RPNs. Develop action plans to mitigate or eliminate the root causes of high-risk failure modes.
This involves implementing new process controls, improving existing processes, redesigning products, or enhancing training.
12. Prioritize actions to deal with failure modes:
Execute the action plan and implement necessary changes to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified failure modes. Ensure proper communication and training to affected stakeholders.
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of implemented changes. Track key metrics and indicators to ensure the desired improvements are achieved. Regularly review and update the FMEA as needed, and consider new information or changes in the process.
Benefits of Failure Mode Effect Analysis
- FMEA helps in identifying potential failures early in the development or improvement stages of a process or product. By doing this you can proactively address these issues before they occur which ultimately saves time and resources in the long run.
- By systematically analyzing failure modes and their potential effects, it helps in assessing and prioritizing risks. This helps you focus your efforts on mitigating the most critical risks first and reduce the likelihood of costly failures or defects.
- It encourages a thorough examination of the design of a product or process leading to improvements and optimizations. You can make design changes to enhance reliability, efficiency, and performance.
- Through mitigation of potential failure modes, FMEA helps in ensuring that products and processes meet or exceed customer expectations. By delivering more reliable and high-quality products/services your organization can enhance customer satisfaction.
- It helps in avoiding costs associated with rework, scrap, warranty claims, and customer complaints. Investing time and resources in FMEA can lead to significant cost savings over the lifecycle of a product or process.
- For industries with stringent regulatory requirements like healthcare or automotive, this tool helps organizations demonstrate compliance by systematically assessing and managing risks associated with their products or processes.
If you are looking for practical training to learn Lean Six Sigma methodology and get certified in Lean Six Sigma then I would like to recommend you best practical live training program check out – Lean Six Sigma with Minitab live training program and certification.
Conclusion
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is not just a skill but a strategic tool for organizations committed to delivering high-quality products and services while minimizing risks.
Through systematic identification, evaluation, and mitigation of failure modes using FMEA, organizations can proactively safeguard their processes, products, customer trust, and reputation.
By fostering a culture of proactive risk management and data-driven decision-making, FMEA empowers organizations to stay ahead of the curve in today’s competitive business environment by saving time and resources.
If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to get more such articles every week.





Excellent article, it helped me clarify some doubts.
Thanks for your feedback!