Imagine a scenario where a machine not only performs its assigned tasks but also possesses the intelligence to identify defects or abnormalities as they occur. That’s the function of Jidoka autonomation also called automation with human touch.
This tool signifies the empowerment of frontline workers to detect abnormalities, stop production, and initiate problem-solving immediately to prevent defects from occurring. Ultimately streamlines processes, reduces waste, and enhances overall process efficiency
In this article, I will discuss the core principles of Jidoka Autonomation, its historical evaluations, and its application across different industries, and at the end also discuss how this powerful lean tool works.
Whether you are a lean practitioner or new to the lean world this article will help you understand the concept of automation with human touch. So are you ready to implement Jidoka Autonomation at your organization? Then let’s get started…
What is Jidoka Autonomation?
Jidoka is one of the fundamental concepts in Lean Manufacturing philosophy you can call it as automation with the human touch. It was pioneered by Toyota as a part of the world-famous Toyota Production System and their approach to quality control.
Jidoka is 2 Japanese word combinations in which Ji means Automation and Doka means without irregularities or stopping. That’s why it is called Jidoko autonomation means automation with the human touch.
It signifies the combination of automation with human intelligence and intervention when needed. Instead of relying solely on machines to run continuously this tool emphasizes building intelligence into the process to empower both machines and workers to ensure quality.
One of the key aspects of this tool is the ability to detect abnormalities or deviations from the standard. This could be anything from equipment malfunctions to defects in the product being manufactured.
The goal is to catch these issues as soon as they occur instead of letting them propagate through the process. Once the abnormality is detected, jidoka enables an autonomous response.
This could involve stopping the machine, signaling for assistance, or initiating corrective action. The idea is to prevent the production of defective products or if a defect has already occurred, prevent them from further processing of the defective items.
Along with autonomous response jidoka also emphasizes the importance of human involvement. Workers/employees are trained to monitor the process closely and intervene when necessary.

This could involve investigating the cause of the abnormality, making adjustments to the equipment, or implementing improvements to prevent similar issues in the future.
By integrating this powerful lean tool into the process, companies can build quality into their products from the beginning. Instead of relying on inspection at the end of the process to catch defects, jidoka focuses on preventing defects from occurring in the first place.
This improves product quality as well as reduces waste and rework. By constantly monitoring for abnormalities and addressing root causes, the organization can refine its processes over time to become more efficient and effective.
4 Principles of Jidoko Autonomation:
1. Discover an abnormality:
This principle emphasizes the importance of being vigilant and proactive in identifying abnormalities or deviations from the standard in the process.
This could be anything that doesn’t align with the expected quality standards such as defects, malfunctions, or deviations from the specified process parameters.
Every member of the team needs to be trained to recognize these abnormalities whether they are on the frontline workers, supervisors, or managers.
2. Stop the process:
Once an abnormality is identified the next principle says to immediately stop the process. This is a critical aspect of Jidoka as it prevents defective products from being produced further down the line.
By stopping the process as soon as the issue is detected the organization prevents the creation of more defects, thereby minimizing waste and rework. It also helps in containing the problem and preventing it from escalating and affecting downstream processes.
3. Fix the immediate problem:
After halting the process, the focus shifts to addressing the immediate problem. This involves taking quick and effective action to rectify the abnormality and ensure that the process can flow smoothly.
The goal here is to restore the process to its normal state as rapidly as possible. This may involve simple fixes or adjustments that can be implemented on the spot by the frontline workers or technicians.
4. Investigate and solve the root cause:
While fixing the immediate problem is essential for getting the process back on track, it’s equally important to delve deeper into the root cause of the abnormality to prevent its recurrence in the future.
This requires conducting a thorough investigation to identify the underlying factors or systematic issues that led to the deviation from the standard.
By addressing the root cause, the organization can implement long-term corrective actions to prevent similar issues from occurring again thereby improving overall process reliability and efficiency.
Key Components of Jidoka Autonomation
Let’s see the components of Jidoka autonomation that help organizations achieve a higher level of efficiency, quality, and flexibility in their processes while empowering employees to contribute to continuous improvement efforts.
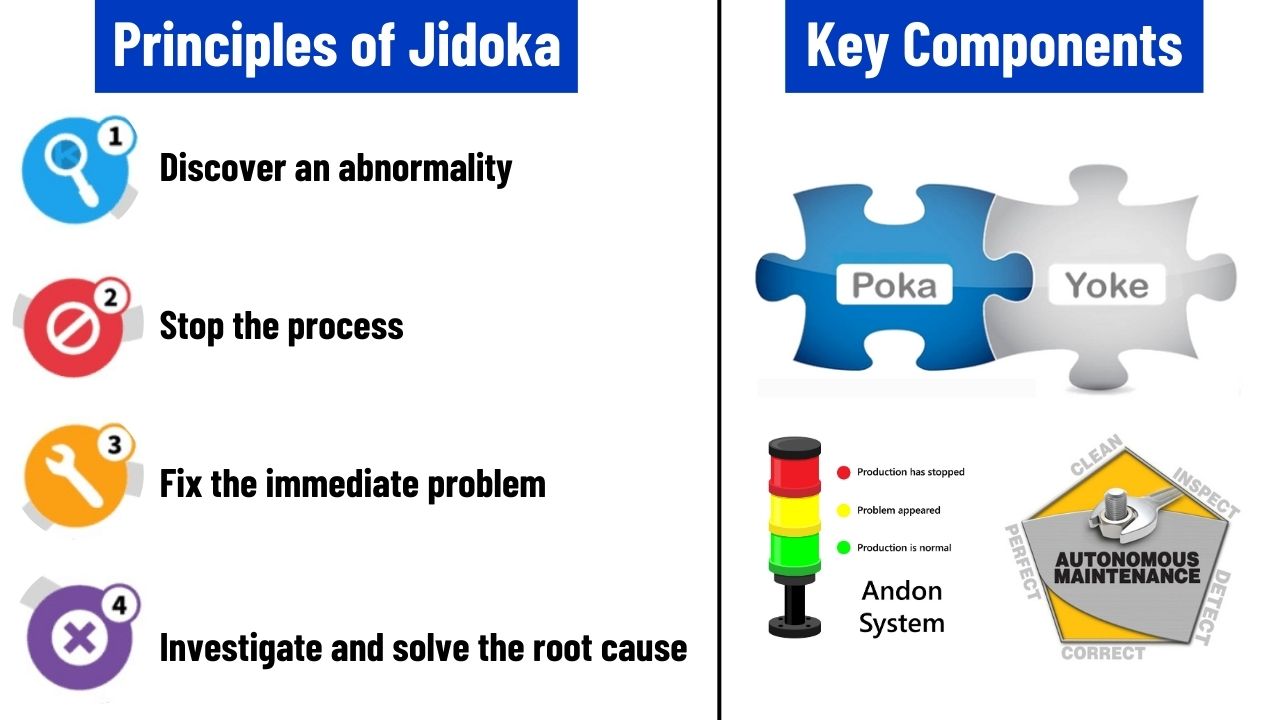
Poka-yoke:
Mistake-proofing mechanisms are designed to prevent errors or defects during the process. These systems can be physical devices or procedural steps that ensure tasks are performed correctly every time and reduce the likelihood of defects.
By incorporating poka-yoke systems manufacturers minimize rework, waste, and defects thereby improving overall product quality and efficiency.
Andon system for visual management:
Andon system provides real-time visual cues and alerts to indicate the status of processes. They typically use lights, sounds, or displays to signal abnormalities and allow workers to identify and respond to issues in the process quickly.
Andon’s system promotes transparency, communication, and problem-solving by enabling workers to escalate problems and collaborate on solutions promptly. This tool helps maintain the smooth process flow alert type signals.
Autonomous maintenance:
Autonomous maintenance involves empowering frontline workers/employees to take ownership of equipment upkeep and minor repairs.
By training workers to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting machinery, organizations can prevent breakdowns and maintain consistent quality.
This fosters a proactive approach to equipment care reduces the reliance on specialized maintenance staff and promotes a sense of responsibility among workers for the overall equipment effectiveness and process outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in Jidoka Autonomation
When organizations address the challenges proactively and systematically, they can successfully implement Jidoka autonomation and drive continuous improvement in the process.
There are some common challenges one can face while implementing Jidoka. Let’s see them one by one and understand how to overcome those challenges:
1. Resistance to change:
This is one of the most common challenges when introducing new processes or technologies, especially in manufacturing environments where employees may fear job losses or disruptions to their routines.
- Clearly articulate the reasons for implementing jidoka autonomation such as improved quality, increased productivity, and enhanced job satisfaction.
- Encourage participation and input from frontline employees in the design and implementation phases. This makes them feel valued and ultimately reduces resistance from their side.
- Offer training programs to help employees develop the skills needed to operate and maintain automated systems. Address any concerns or misconceptions through open dialogue.
2. Lack of understanding among the employees:
When employees don’t know about what Jidoka autonomation is and how it helps the organization then it’s difficult to convince them of its implementation. You can improve their understanding of Jidoka using the following ways…
- Provide clear explanations of how Jidoa works and its potential benefits for both the organization and individual employees.
- Emphasize the importance of innovation and problem-solving, highlighting how jidoka autonomation aligns with lean principles.
- Acknowledge the efforts of employees who actively support the implementation of Jidoak autonomation and reinforce the positive attitude towards change.
3. Technical hurdles in implementation:
Technical challenges can arise during the implementation of automated systems such as integration issues or unexpected downtime. You can overcome that using the following ways:
- Invest time upfront to assess the technical requirements and potential obstacles associated with implementing jidoka autonomation.
- Work closely with automation vendors, engineers, and IT professionals to address technical challenges and ensure smooth implementation.
- Start with small-scale pilot projects to identify and resolve technical issues before full-scale implementation. This allows for adjustments to be made without disrupting operations.
4. Sustaining improvement over time:
Maintaining and sustaining the improvements in Jidoka autonomation requires a commitment from the employees.
- Define KPIs to monitor the effectiveness of jidoka and track progress over time.
- Schedule periodic reviews to assess the performance of automated systems, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments.
- Keep employees involved and informed about the benefits of Jidoka consistently and encourage their participation in improvement efforts.
- Encouraging flexibility and openness to change, allows the organization to respond quickly to evolving challenges and opportunities.
Benefits of Automation with Human Touch
Let’s see what makes this Lean tool so much powerful. Here are some of the major benefits this lean tool offers because of which organizations believe in its implementation.
- The main benefit of Jidoka Autonomation is its ability to detect defects as soon as they occur. By implementing sensors, visual aids, or other detection mechanisms within the production line, abnormalities and defects can be identified in real-time.
- This allows operators to intervene immediately and prevents the production of defective parts or products. Early detection helps minimize the waste and reduces the need for costly rework, or repairs.
- Jidoka promotes the idea of stopping the line whenever an abnormality is detected. Rather than allowing defects to propagate through the process, production is halted automatically and ensures that no further defective parts are produced.
- This emphasis on built-in quality ensures that every product meets the required standards, which leads to higher customer satisfaction and reduced costs associated with defects.
- Jidoka automation empowers frontline workers/employees by giving them the authority to stop the production line when they identify a problem. This encourages a sense of ownership and accountability among employees.
- This makes operators or employees more actively engaged in the process, and participate in the problem-solving and root causes analysis to address issues at their source.
- Jidoka automatically stops production when defects occur and with that, it prevents the production of defective parts, ultimately this saves valuable resources such as time, materials, and labor.
- Instead of allowing defects to pass through multiple processes and incur additional costs, resources can be allocated more efficiently to maintain high levels of productivity and profitability.
- Jidoka also reduces the variability in the process by addressing abnormalities promptly. By standardizing the response to deviations from the norm, it promotes consistency and stability in the process.
- This leads to smooth workflows, shorter lead times, and increased predictability that ultimately enhances overall efficiency and process performance. In the end, this tool helps in continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Jidoka autonomation gives frontline workers the authority to stop the production line when abnormalities arise, this not only enhances product quality but also fosters a culture of ownership and accountability.
This culture shift due to Jidoka autonomation empowers employees to take proactive measures to address quality issues promptly, driving overall process improvement that results in waste elimination and defect reduction.
It represents a holistic approach where technology and human expertise complement each other. With the help of this powerful lean tool organizations can optimize their processes, enhance productivity, and ultimately deliver greater value to customers.
If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to get more such articles every week.