Just like in a winning sports team, various people who have specific positions or roles, they have defined responsibilities. Six Sigma roles and responsibilities are also similar, each person is trained to be able to understand and perform the responsibilities of their role while working on a six sigma project.
Enterprises with successful Lean Six Sigma programs have found it useful to distribute roles and responsibilities for various people involved in project activity in order to improve the productivity of the team. In this article, we are going to discuss Six Sigma Roles and Responsibilities in detail so let’s start…
Roles of Six Sigma project team –
Any Six Sigma team usually has 6 types of personnel and three levels of reporting structure. The internal communication of the Six Sigma team is highly informal. This is because every project has different requirements and the work cannot be generalized. ( Check out communication strategies for six sigma)
However, before the beginning of any project roles and responsibilities are assigned to every person in the team. Look at this picture it shows the major roles of the Six Sigma team –
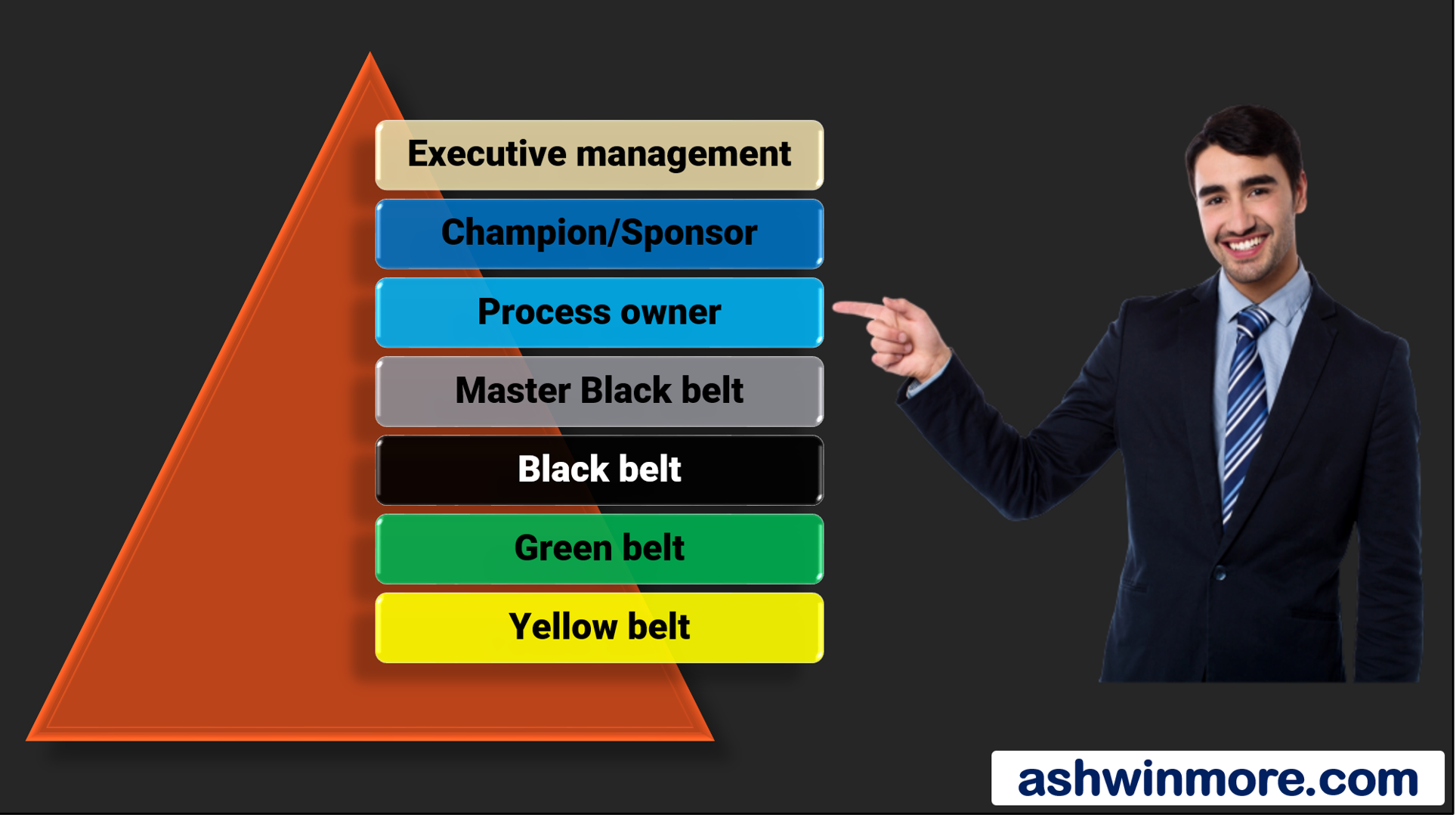
Read more –What is Six Sigma methodology?
Read more – What is Lean manufacturing?
Executive management –
The leadership model that is most effective in the deployment of Lean Six Sigma envisions the leader as a problem solver. A leader’s job is to implement systems that identify and solve problems that improve the effectiveness of processes.
This concept of leadership implies an understanding of team dynamics and Lean Six Sigma problem-solving techniques. Deployment of any culture-changing initiatives like adopting Lean Six Sigma rarely succeeds without management support that’s why it is important to have top management support for the successful implementation of Lean Six Sigma.
The executive leadership owns the vision for the business, they provide sponsorship and set expectations for the results from Six Sigma.
They enable the organization to apply Six Sigma and then monitor the progress against expectations. They typically receive specialized Lean Six Sigma training to support their role.
Primary responsibilities of Executive leadership:
- Makes the decision to implement the Lean Six Sigma initiative and develop an accountability method.
- Setting the vision and overall objectives for the initiative.
- Setting the direction and priorities for the Lean Six Sigma organization.
- Approving the project selection methodology.
- Selecting and suggesting the projects.
- Ensuring projects are aligned to organizational strategy.
- Selecting project champions.
- Allocating resources for projects.
- Monitoring the progress of the Lean Six Sigma initiative.
- Eliminate the organizational barriers and reward successful projects.
Champion –
Champion is typically an upper-level manager and also called “sponsor”, who identifies and selects the most meaningful projects to work on, also provides guidance to the six sigma belts and opens doors for the belts to apply process improvement technologies.
They are responsible for a business roadmap and employee training plan to achieve the goals and objectives of Six Sigma within their area of accountability. They also receive specialized Lean Six Sigma training to support their role.
Primary responsibilities of Champion:
- They approve and sign off the project charter.
- They approve and sign off the project charter.
- Serves as the liaison between the team and senior management.
- Ensures his /her projects are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. Also terminates those projects which are not aligned.
- Provides resources to the Lean Six Sigma teams.
- Removes organizational barriers for the team.
- Leads project tollgate reviews.
- Asks appropriate questions to the project team and approves completed projects.
- Provides reward and recognition to the project team members.
- Leverages (replicates) project results.
Process owner –
A process owner is a Lean Six Sigma role associated with an individual, who coordinates the various function and work activities at all levels of the process.
He has the authority or ability to make changes in the process as required or to make decisions regarding process changes and manages the entire process cycle so as to ensure performance effectiveness.
They should be involved in any discussion of process change, most of the time they are willing to support changes but need to see evidence that recommended improvements are for the long-term benefits of the enterprise.
In many cases, the process owner acts as a project champion so they also receive Lean six sigma training at least up to green belt level to support their role.
Primary responsibilities of process owner –
- Select team members.
- Allocation of resources for projects.
- Provides process knowledge.
- Review process changes.
- Approve and support the process changes.
- Implements process changes.
- Take responsibility for the execution and maintenance of the control plan.
Ensures that improvements are sustained.
Master black belt –
A Master black belt is an individual, who is a technical expert of six sigma methodologies and he has advanced knowledge in statistics as well as other project management fields so he provides technical support/mentorship to the Black belt and Green belt during the project.
MBB’s are usually authorizing bodies to certify black belts and green belts, they need to have an ability to influence change and motivate others.
Master black belt projects may be of equal or greater complexity to those undertaken by the Black belt, in addition to the projects they are capable of conducting training, consulting, and teaching Lean Six Sigma tools and practices to others.
Primary responsibilities of Master black belt:
- Coach Six Sigma Black belts and Green belts.
- Utilize the resources provided by management effectively.
- Monitor project progress closely.
- Work with Champion and Process owner for the selection of projects.
- Address issues that cause the project to unstable.
- Remove barriers hindering the success of the project.
- Support as a subject matter expert for the organization as well as improvement projects.
- Review and approve completed projects.
- Share all the lessons learned with the project team.
- Provide inputs to the reward committee after project completion.
Read more – Lean vs Six Sigma: important differences.
Black belt –
A Black belt is a project team leader, working full time to solve problems under the direction of a champion and with technical support from a Master Black belt. Black belt work on projects that are relatively complex ad require significant focus to resolve.
Most of BB’s conduct an average of 4 to 6 projects per year, projects that usually have a high financial return for the company. They are application experts and well versed with the Six Sigma methodologies and they have the ability to drive the results.
Primary responsibilities of Black belt:
- Lead and manage Six Sigma projects.
- Provide net present value, return on investment, payback calculations on projects.
- Utilize the resources provided by management effectively.
- Monitor project progress closely.
- Facilitates DMAIC teams in applying Six Sigma methods to solve problems.
- Work with the Champion, Process Owner, and Master black belt for the selection of projects.
- Address issues that occurred during the project and consult with the Master Black belt.
- Update and present project progress to management.
- Review completed projects.
- Share all the lessons learned with the project team.
Read more – What is DMAIC methodology?
Green Belt –
Green belts are practitioners of Six Sigma methodology and typically work within their functional areas or support larger Black belt projects. They are capable of solving problems within their local span of control.
They usually address less complex problems than Black belts and perform at least 2 projects per year. They also are a part of the Black belt team and help to complete the Black belt project.
Primary responsibilities of Green belt:
- Support Six Sigma projects with higher ROI.
- Lead smaller projects with moderate saving and ROI.
- Supporting projects with process knowledge and data collection.
- Follow the DMAIC process and apply appropriate statistical methods.
- Involved in identifying improvement opportunities with a Black belt.
- Provides inputs to the Master Black belt, Black belt, and process owner during the selection of projects.
- Identify and report the barriers hindering the success of the project and consult with MBB, BB.
- Lead small-scale projects under the guidance of Black belts.
Read more – What is Green belt Six Sigma certification?
Yellow belt –
Yellow belt participates in process management activities. They fully understand the principle of Six Sigma and are capable of characterizing processes, solving problems associated with their work responsibilities, and implementing and maintaining the gains from improvements.
They apply Six Sigma concepts to their work assignments. They may participate in Green or Black belt projects.
Primary responsibilities of Yellow belt:
- Provide support to the Black belt and Green belt during projects.
- Being an effective team member always supports the project in the data collection process.
- Follow the DMAIC process and apply appropriate tools.
- Use Six Sigma tools in the workplace.
- Make a suggestion for future projects.
Along with this, there are other team members in a project team who are selected by the process owner and trained in six sigma methodologies. They actively support and contribute to Six Sigma projects.
Get certified in Lean Six Sigma – IASSC/ASQ Lean Six Sigma Training program
Conclusion –
These are some of the important six sigma roles and responsibilities in projects that you need to be aware of. It’s important that each team should know their roles and for which tasks they are responsible in the six sigma projects.
Because overlap in the roles and responsibilities may cause confusion in the team and that may result in a delay in the project work. But when six sigma roles and responsibilities are clearly defined then the six sigma project team works effectively and hence the project work is done easily.
If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to the blog to get a weekly article.






Pingback: Six Sigma certification: Top 15 reasons why you should go for it