Process improvement is a strategic decision to achieve this, the two best methodologies stand out i.e. DMAIC vs DMADV. Choosing the right Six Sigma methodology makes a difference in process improvement initiatives at the organization.
DMAIC is a data-based problem-solving methodology used for improving existing processes. On the other hand, DMADV is a design thinking-based problem-solving methodology used for developing new processes or products.
The ultimate purpose of both these methodologies is to drive continuous improvement and innovation in the organization. In this article on DMAIC vs DMADV, we will understand both these approaches in detail along with their strengths and applications.
Whether you want to refine the existing processes or develop new processes/products, understanding (DMAIC vs DMADV) which methodology aligns with your organizational goal is super important. Let’s get started…
What is the DMAIC methodology?
The most powerful and popularly used Methodology in Lean Six Sigma is DMAIC. It is the structured data-driven problem-solving approach used to improve existing processes in the organization and achieve measurable as well as sustainable results.
The acronym stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. This 5 step methodology is iterative, involves cross-functional teams, and can be applied in different business processes to achieve continuous improvement and quality outputs.
Throughout the DMAIC phases, Lean Six Sigma practitioners use different tools and techniques during each phase for improve and controlling processes. Let’s see the overview of each phase of DMAIC (before DMAIC vs DMADV). (Check out – DMAIC methodology in detail)

1. Define phase:
This phase clearly states the problem or opportunity for improvement and defines the process improvement project scope.
Activities:
- Identify the process to be improved.
- Define the problem statement, project goal, and objectives.
- Identify the key project stakeholders and their expectations.
- Develop the high-level process map to understand the current state of the process.
Output of Define phase:
- Project charter with complete details like project scope, objectives, team members, problem statement, and timelines.
- High-level process map.
2. Measure phase:
The focus of the measure phase is to quantify the current state of the process. This involves collecting data to establish a baseline and understand the performance of the process.
Activities:
- Identify the key process metrics (Critical to Quality or CTQs)
- Collect data on the current process performance.
- Validate measurement system capability (if needed).
- Develop detailed process maps.
- Calculate baseline process capability.
Output of Measure phase:
- Baseline data on process performance.
- Identified process capability and stability.
3. Analyze phase:
At this phase, the project team analyzes the data collected in the measure phase to identify the root causes of the problem and opportunities for improvement.
Activities:
- Conduct a detailed data analysis.
- Identify the patterns, trends, and anomalies in data.
- Conduct root cause analysis using tools like fishbone diagram and 5 Whys analysis.
- Validate root causes through data and process analysis.
- Prioritize root causes based on importance and feasibility.
Output of Analyze phase:
- Identified root causes of the problems.
- Clear understanding of the current state of the process.
4. Improve phase:
At this phase, the potential solutions to address the identified root causes of the problem are developed and implemented to improve the process.
Activities:
- Develop potential solutions to address the root causes.
- Evaluate and select the best solutions.
- Develop an implementation plan.
- Implement the solutions.
- Conduct a pilot test if needed.
- Monitor and measure the results.
Output of Improve phase:
- Improved process design.
- Implemented final solutions.
5. Control phase:
This phase involves putting measures in place to sustain improvements achieved in the improve phase. It ensures the improvements are sustained for a long time and the process remains in control.
Activities:
- Develop control plans and standard operating procedures.
- Implement monitoring systems to track key process metrics.
- Train and empower employees to sustain improvements.
- Add a response plan for any issue in the process.
Output of Control phase:
- Control plan and monitoring systems.
- Sustained process improvements.
Benefits of DMAIC methodology:
Before understanding the differences between these 2 methodologies (DMAIC vs DMADV) let’s see some of the major advantages of the DMAIC methodology.
- DMAIC emphasizes the importance of data and facts in decision-making that reduces the reliance on assumptions and opinions during process improvement projects.
- This problem-solving methodology focuses on meeting customer requirements and expectations by continuously improving processes and that results in improved customer satisfaction.
- DMAIC provides a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement with 5 powerful phases and a proper sequence of steps.
- This methodology fosters a culture of continuous improvement by systematically addressing the issues and optimizing processes over time.
- The main focus of DMAIC is to eliminate defects/waste in the process and reduce process variation so by doing this DMAIC helps the organization in significant cost savings and improved profitability.
- DMAIC encourages collaboration among different departments and functions within an organization, that fosters a team-based approach to problem solving.
What is the DMADV methodology?
The 2nd powerful structured methodology used in Lean Six Sigma is DMADV. This methodology helps organizations develop new processes or products with a high level of quality, efficiency, reliability, and alignment with customer needs from the beginning.
It is useful where existing processes are not sufficient and the goal is to create totally new processes/products or completely redesign the existing processes to meet high-performance standards with better results.
DMADV stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify, also known as Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) methodology. In the upcoming article, I will discuss DMADV in detail but for now, let’s see the overview of each phase of DMADV (before DMAIC vs DMADV).
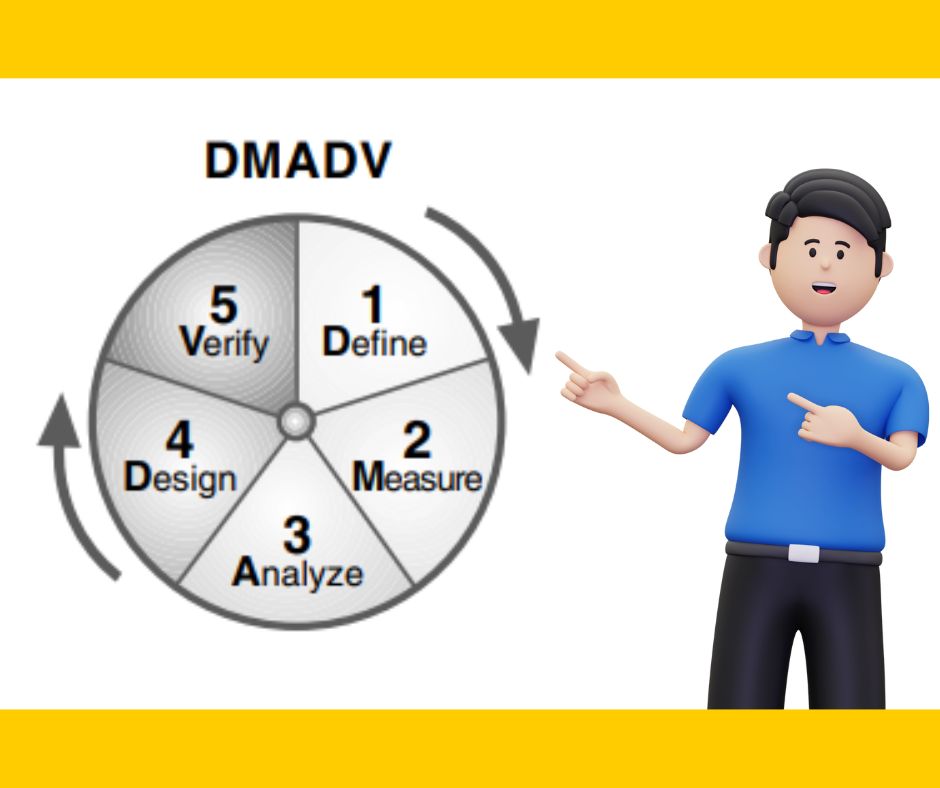
1. Define phase:
In this phase, the project goals and objectives are defined and the scope of the project is outlined by understanding customer needs.
Activities:
- Identify and define the goals of the project.
- Define the project scope and boundaries.
- Identify the key factors that are crucial for meeting customer requirements.
- Develop the high-level process map.
Output of Define phase:
- Project charter for DMADV project.
- High-level process map.
- Identified customer needs and specifications.
2. Measure phase:
This phase involves measuring and quantifying the current state of the process or products to see where improvements can be made.
Activities:
- Identify the critical to quality (CTQ) factors.
- Define measurement systems and metrics.
- Collect data related to the process or product.
- Establish baseline performance.
Output of Measure phase:
- Data collection plan.
- Baseline performance metrics.
- Identified CTQs.
3. Analyze phase:
In this phase, analyze the data collected during the measure phase and determine which factors are most influential in achieving the desired outcome from the process.
Activities:
- Identify and analyze potential failure modes in the new design.
- Conduct a risk analysis.
- Use tools to identify significant factors affecting the new process performance.
- Develop and evaluate design concepts.
Output of Analyze phase:
- Cause and effect relations diagram.
- FMEA analysis.
- Risk analysis results.
4. Design phase:
This phase focuses on developing and designing new processes or products to meet the defined project goals or you can say meet the customer needs and then test it.
Activities:
- Develop detailed design specifications.
- Design the new process, product, or service based on the analysis.
- Optimize the design for performance and efficiency.
- Create prototypes and conduct simulations if necessary.
Output of Design phase:
- Detailed process design documentation.
- Risk mitigation plan.
5. Verify phase:
In this phase, verify that the designed products or process meets the customer input requirements. Also, validate how the designed process works under real or simulated conditions.
Activities:
- Validate the new process/product design through pilot programs or simulations.
- Conduct testing and validation to ensure the design meets customer requirements.
- Implement the new process, product, or service.
- Establish a control mechanism to monitor ongoing performance.
Output of Verify phase:
- Pilot testing results.
- Full-scale implementation plan.
- Customer verification that the new design meets specifications.
Benefits of DMADV methodology:
Before understanding the differences between these 2 methodologies (DMAIC vs DMADV) let’s see some of the major advantages of the DMADV methodology.
- DMADV focuses on defining customer needs and expectations early in the process so that organizations can design products or processes that better satisfy customer requirements.
- This methodology involves a systematic approach to design and verification that helps in identifying and addressing potential issues early in the development process.
- DMADV aims to design processes that are not only defect-free but also efficient and effective in delivering quality outputs. This results in improved overall performance and resource utilization.
- This approach allows the organization to identify and mitigate risks associated with the new product or process development. By dealing with risks proactively, this approach reduces the chances of process/product design project failure.
- The structured design approach of DMADV helps streamline the development process reducing the time it takes to bring a new product to market or a new process to the organization.
- This methodology encourages a creative and innovative approach to problem-solving during the design stage of a process or product. This can lead to the development of a unique and better solution that meets customer needs effectively.
DMAIC vs DMADV: Comparative Analysis
You know the biggest difference between DMAIC vs DMADV is the goals the project team sets and the outcomes of the completed project.
DMADV project might feel like it has a more tangible outcome, but in reality, both methodologies deliver better quality, efficiency, more profits, and higher customer satisfaction.
Let’s understand some of the major differences between the DMAIC vs DMADV approaches so that you can select the right approach as per your project requirement.
| Parameter | DMAIC methodology | DMADV methodology |
| Scope | Used for Improving existing processes. (Incremental improvements) | Used for designing new processes or products. (Radical improvement and Innovation) |
| Focus | Focus on identifying and eliminating the causes of defects or variations in the process. | Focus on creating new, optimized processes or products that meet customer needs. |
| Timeline | Typically has a shorter timeline as it deals with improving existing processes. | Often requires a longer timeline due to the involvement of design and verification phases for new processes. |
| Flexibility | More flexible and adaptable to a wide range of improvement projects within existing processes. | More structured and may be perceived as rigid, but it provides a systematic approach to designing and implementing new processes. |
| Risk | Generally low risk since it deals with existing processes that have known issues. | Involves higher risk as it deals with the creation of something new and uncertainty may arise during the design and implementation phases. |
| Data availability | Relies on historical data from existing processes. | Involves more predictive analysis and requires market research, simulations, and pilot studies for new designs. |
| Change management | Emphasizes the need for effective change management to ensure improvements are sustained. (Corrective approach) | Emphasizes on building in quality from the beginning, reducing the need for significant changes post-implementation. (Preventive approach) |
| Project start | Typically initiated in response to a problem or set of identified issues with an existing process. (Reach approach) | Started proactively to design a new process or product, often in response to market opportunities. (Proactive approach) |
| Tools and Techniques | Use tools like process mapping, root causes analysis, statistical process control, and hypothesis testing. | Use tools like the Kano model, quality function deployment, and failure mode effect analysis. |
| Applicability | Applicable to processes with identified issues or inefficiencies that need to be addressed for improvement. | Applicable when starting to design new processes or products from scratch where no existing baseline is available. |
Examples to understand which methodology to use between DMAIC vs DMADV:
Example: A business wants to create a smartphone app to help customers make and manage appointments.
For this DMADV approach is best as they are creating a product that doesn’t yet exist. The app itself is a new product and process. That app will need to be designed, integrated into the existing system, and the final product tested before full implementation.
Example: A doctor’s office has had a lot of complaints from patients because it is too hard to get appointments, appointment communications are confusing or patients show up for an appointment and are told they don’t have an appointment.
For this DMAIC approach is best as this is an existing process that needs improvement. The team continues with the DMAIC process and modifies the activities in each phase to fit the needs of the project at hand.
If you are looking for practical training to learn the DMAIC approach and get certified in Lean Six Sigma then I would like to recommend you best practical live training program check out – Lean Six Sigma with Minitab live training program and certification.
Similarities between DMAIC and DMADV
Now you know the DMAIC vs DMADV differences, let’s understand some important similarities between these two powerful Lean Six Sigma methodologies.
- Both DMAIC and DMADV provide a structured and systematic set of 5 phases to guide projects from start to end. These phases help in proper problem-solving and process improvement.
- Whether you want to improve an existing process (DMAIC ) or design a new process (DMADV) both these need a proper understanding of the customer needs and requirements.
- Both these methodologies rely on data and statistical analysis for making informed decisions during DMAIC projects as well as DMADV projects.
- Both DMAIC and DMADV encourage the use of cross-functional teams to bring diverse perspectives and expertise for process improvement and process/product development projects.
- Both DMAIC and DMADV methodologies incorporate project management principles to ensure that the projects are well-planned, executed, and monitored.
- Most of the tools and techniques used during DMAIC and DMADV projects are similar. Even if these two DMAIC vs DMADV approaches are used for different applications still there are a lot of similarities between these two methodologies.
Conclusion
Both methodologies are important parts of Lean Six Sigma, it’s a matter of selecting the one that aligns with your organizational goals. Understanding your organizational goals and project scope is essential to selecting the right methodology between DMAIC vs DMADV.
DMAIC is useful when your aim is to enhance efficiency, seek incremental improvements, and reduce defects. On the other hand, if the aim is to develop new robust processes/products and drive innovation then the DMADV approach is useful.
In this article, I discussed the key major differences as well as similarities between the 2 most powerful Lean Six Sigma methodologies (DMAIC vs DMADV). Also gone through the overview of each phase of both DMAIC and DMADV.
Now I hope you can select the right methodology as per your requirements. If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to get more such articles every week.







Great post, excellent explanation about these important methodologies of lean six sigma, really is useful for new people and practioners
Thanks for your feedback!
dear sir
i am black belt,
really your site and your courses are good and useful
thanks so much
Your welcome! Thanks for your feedback.