Many of my friends ask me a question what is Six Sigma and how it is useful for businesses? well, this is the reason I am writing this comprehensive article on Six Sigma so that beginners also understand it easily.
A Six Sigma approach, you can call it whatever you want, a methodology, improvement tool, problem-solving technique, or business strategy, this all-rounder approach has changed many worst-performing companies into highly profitable companies like Motorola, Allied Signal, and General Electric by improving their business processes.
It has become one of the most popular problem-solving management approaches in today’s competitive market which helps businesses to grow faster.
This Six Sigma approach has been adopted by a growing majority of Fortune 500 companies as well as many small and mid-sized organizations.
Its application in both for-profit and non-profit organizations is a reflection of its broad objectives in improving processes at the core of an organization’s mission and till now it helped so many organizations in the long-term growth.
In this article, we will discuss what is six sigma, Starting from its meaning up to its application in different fields. so let’s get started…
History of Six Sigma:
The history of this methodology encompassed various events that shaped its formation and spread. The roots of Six Sigma are commonly attributed to the companies like Toyota and Motorola.
When a Japanese firm took over a Motorola factory that manufactured Quasar television sets in the United States in the 1970s, they promptly set about making drastic changes in the way the factory operated.
Under Japanese management, the factory started producing TV sets with a huge reduction in defects as they had produced under Motorola’s management.
They did this using the same workforce, technology, and designs, and the main thing is they achieved all this at lower costs, this positive result of Japanese management made it clear that there was something wrong with Motorola’s management.
Finally, Motorola’s executives also admitted that ” we are lacking in maintaining quality” and then it took 10 years for Motorola (in the mid-1980s) to figure out what to do about this.
Bob Galvin, Motorola’s CEO at the time, again started the company on the quality path known as Six Sigma and became a business icon largely as a result of what he accomplished in quality at Motorola, that’s how this methodology came into existence.

By using Six Sigma Motorola became a Quality leader and also won the prestigious “Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award” in 1988, after that the secret of Motorola’s success became public knowledge, and then onwards Six Sigma revolution was started.
After Motorola, many companies like Allied Signal, and General Electric implemented this methodology and produced profitable results.
Currently, it is more popular than ever, now it has been embraced worldwide as a powerful and effective process improvement methodology.
Six Sigma definition-
Sigma is a letter in the Greek alphabet used by statisticians to measure the variability in the process. It has become Six Sigma, a methodology for process improvement and a statistical concept that seeks to define the variation inherent in any process.
It is a data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects in any process from manufacturing to transactional and from product to service-based.
It is a defined and disciplined business methodology to increase customer satisfaction and profitability by streamlining operations, improving quality, and eliminating defects in every process of the company.

It is the only methodology available in the market that is a structured step-by-step methodology designed to solve any business problem because it clearly defines what needs to be done in the process, how it needs to be done, and by when.
The comprehensive premise of this methodology is that “Variation in the process leads to opportunities for error, opportunities for error then lead to risk for product defects, product defects lead to poor customer satisfaction.” So by working to reduce variation and opportunities for error, this method ultimately reduces process cost and increases customer satisfaction.
Jack Welch (former CEO of GE) put it in simple words that “Six Sigma is a quality program when all is said and done, improves your customer experience, lowers your cost and builds better leaders.” that means the ultimate focus of this methodology is to make processes more capable through the reduction in variation and by removing defects in the final product or service, increase customers satisfaction.
Statistical meaning of Six Sigma –
The term Six Sigma is drawn from the statistical discipline ‘process capability studies’. As we know Sigma is represented by the Greek alphabet ‘σ’, which stands for standard deviation from the mean. It represents six standard deviations from the mean.
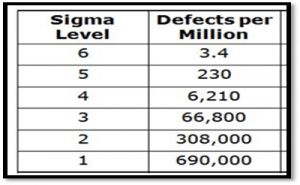
This implies that if a company produces 1,000,000 parts/units and its processes are performing at the Six Sigma level, then in the end only 3.4 defects will occur. so we can say that in the Six Sigma process there are only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
However, if the processes are at the three-sigma level then the company ends up with as many as 66,807 defects for every 1,000,000 parts/units produced. So in the three-sigma level process, there are 66,807 defects per million opportunities.
Similarly, for the two-sigma level process, there are 308,507 defects per million opportunities, etc. So by knowing defects, we can find at what level of sigma our process is performing. Sigma levels provide an organization with a high-level look at how effective the process is performing.
Now see the below table which shows the number of defects observed for every 1,000,000 parts produced along with their respective sigma level.
There is one more factor that is important to understand the meaning of the Six Sigma level process and that parameter is process yield.
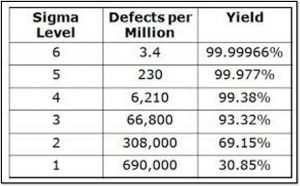
In the Six Sigma process, there are 3.4 defects per million opportunities means 99.9996 % of products are without defects, we can say that the process yield of the Six Sigma process is 99.9996%.
Similarly, for the 5 Sigma process, there are 230 defects per million opportunities means 99.97% of products are without defects. again for the 3 sigma process, 93.32% of products are without defects, and for the 2 sigma process, 69.15% of products are without defects.
At last, for the 1 sigma process, 30.85% of products are without defects. Look at the below table. This process improvement approach represents a great deal to a business enterprise.
At the basic level, it is a process improvement toolset yet, when linked to corporate strategy it becomes an operating philosophy of great assistance to the accomplishment of corporate objectives. let’s see now its meaning from a different perspective.
Methodology –
As a methodology to be followed by practitioners, Six Sigma is a standardized approach to problem-solving or opportunity grasping. There are two main methodologies that the Six Sigma approach follows i.e. DMAIC and DMADV
(i) DMAIC approach–
It is the popular process improvement methodology using Six Sigma and it primarily focuses on improving existing processes or products.
This approach yields a focus on cause and effect with analytical problem-solving tools within a management structure to ensure results. Its acronym is given below.
D- Define – Here we need to define the actual problem by understanding customer needs and establishing a project foundation.
The purpose of this phase is to create a project charter that includes a problem statement, goal statement, and business case that is aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
M-Measure – here we need to measure the key aspects of the current process and collect relevant data then check the accuracy and precision of the data.
At last, perform process capability to check how our process performing in terms of meeting customer expectations hence the purpose of this phase is to collect process performance data.
A- Analyze – here we need to Analyze data to confirm cause-and-effect relationships, establish optimal performance settings for each input variable or X’s, and also verify the root causes problem.
I – Improve – here we need to improve the current process using data analysis as a basis for improvement. The purpose of this phase is to test and verify the improvement solution.
C- Control – The purpose of this phase is to establish and deploy a control plan to ensure that improvements made in the process are maintained.

(II) DMADV approach –
DMADV is a well-organized design for Six Sigma methodology and it primarily focuses on creating or designing new processes and products as per Six Sigma standards. its acronym is given below.
D- Define – Define customer or company goals and display what product or process we are going to design.
M- Measure – Measure critical to quality characteristics (customer expectation) and perform a capability study to understand how our product or process will meet customer expectations.
A- Analyze – Analyze the data from our measurements and predict how will be a newly designed process or product.
D- Design – This means carrying out the process of designing a product or process based on the analysis performed in the earlier step. The organization has its policies and procedures for respective design processes and uses tools like prototype models, simulations and pilot runs.
V- Verify – This phase is directed at ensuring that the design output meets the design requirements and specifications. Verification is performed on the final product or process.
These methodologies are used as per the application and different types of tools are used during each phase of the DMAIC as well as the DMADV approach. Six Sigma practitioners know when to use which tool to solve problems using these approaches.

Business strategy –
Six Sigma is also a business strategy that provides new knowledge and capability to employees so they can better organize the process activity of the business, solve business problems, and make better decisions.
Using Six Sigma is now a common way to solve business problems and remove waste resulting in significant profitability improvement.
By reducing waste and variation, expenses are reduced and customer satisfaction increases. Because in addition to improving profitability, customer and employee satisfaction are also important.
As a strategy, it links the outputs of the processes conducted within a company to the expectations of customers.
Six Sigma philosophy –
Six Sigma as a philosophy is based on the theory that reducing variation in process output to stay within limits defined by the customer will yield great returns.
Defects are expensive and competitive advantage is gained by meeting customer expectations, six sigma has been proven to accomplish that objective. It is continuous improvement through the use of data and specific variation reduction techniques.
As a philosophy of operational excellence, Six Sigma has a targeted quality performance level of no more than 3.4 DPMO, we talked about this earlier.
When an output of a process operates at this quality performance, it is said to be a “Six Sigma performing” process. It takes a great deal of effort to achieve this however, these efforts are positively correlated to the operating performance of the company.
“Greater the effort higher the operating performance of the company”
Process measurement –
Six Sigma a process measurement system uses accurate data to analyze process performance and find root causes of defects.
It is basically a process-oriented approach where Six Sigma metrics for significant inputs and outputs are measured, monitored, and managed. This enables employees and companies to take a process-oriented view of the entire business.
Using the various concepts of Six Sigma, key processes are identified, the outputs of these processes are prioritized, the capability is determined, improvements are made and a management structure is put in place to assure the ongoing success of the business.
Improvement tool –
Six Sigma utilizes specific tools for business problem-solving. Six Sigma tools are used to scope and select projects, modify or design new processes, improve current processes, decrease downtime, and improve customer response time, etc. these tools include histogram, Pareto chart, fishbone diagram, control chart, FMEA, and many more.
Throughout the Six Sigma project, different improvement tools are used at different stages of the DMAIC or DMADV approach. The best utilization of these tools produces a quality end result, that’s why as a whole, the Six Sigma methodology is considered an improvement tool.
Principles of Six Sigma methodology-
A principle is a concept or value that is a guide for behavior or evaluation. It is a rule that has to be or is usually followed. The Six Sigma technique is also based on the core principle which is centered around customer satisfaction, see below-
a) Customer focus –
Six Sigma is about improving quality. The first step in that process is defining what quality means from the perspective of the people whose opinions matter the most i.e., customers.
A business needs to measure quality the same way its customer does. By focusing on the customer, a business can improve its product quality.
b) Identify root causes –
To correctly identify a root cause, a complete understanding of the process is necessary. This does not mean just understanding how a process was designed to work.
It means understanding how the process is actually working. To accomplish this we need to have clearly defined goals for data collection.
We must ensure that measurements are accurate and repeatable and also establish a proper data collection system /process.
Once the data is collected, determine whether it is providing the required insights and is meeting the goals that were established. If not then refine the data collection plan and collect additional information.
Once you finalize the data then use it to look for ways to improve or optimize the process by identifying the root cause of variation.
c) Eliminate variation –
After identifying root causes, make changes to the process that will eliminate variation, and thus eliminate defects from the process. Also, look for ways to eliminate steps that do not add value to the customer. This will eliminate waste.
Be proactive in identifying variation and eliminating it. Don’t wait for signs of variation to become obvious. collect data, talk with people, and study the data to find variations in the process that may have become accepted because that’s the way we have always done things.
d) Teamwork –
Six Sigma involves teams and leaders of Six Sigma belts who take responsibility for the Six Sigma process. The people on the team need to be trained in Six Sigma methods, including the Six Sigma measurement methods and improvement tools that will be used.
In addition, they need communication skills so that they can involve, serve, and communicate clearly with both coworkers and customers.
Putting together teams that have members with a variety of skills and backgrounds related to a process will help the team spot variations. The team members involved in the Six Sigma projects are listed below. Check out the full article on Six Sigma roles and responsibilities.
- Executive management
- Sponsor
- Process owner
- Master black belt
- Black belt
- Green belt
- Yellow belt
e) Be flexible and thorough –
Six Sigma requires flexibility in many ways. The business’s management system needs to accept positive changes as well as empower change. Employees should be motivated to adapt to change.
In the beginning, the benefits of the changes should be made clear to workers. This will help to create an environment where change is more readily accepted.
The key to Six Sigma is the ability to change or adapt procedures as needed. In short, the process required for change should not be so complex that workers and management would rather work with a broken process than fix it. This also requires problem-solving to be thorough.
Making sure to understand every aspect of a process like steps, people, and departments involved will help to ensure how the new or updated process works.
f) Clear and effective visual communications –
Six Sigma involves change and change requires effective ongoing communications. Old habits need to be broken and new habits established.
Tools like kaizen can be used to help create an environment where changes are accepted and business practices are continuously improved upon, while 5s can be used to make problems easier to spot as well as create standardized processes.
Benefits of Six Sigma methodology –
This methodology has proven to be successful in many organizations to reduce defects and variation in processes. Its implementation offers lots of benefits to the organization. Let’s have a look at some important benefits –
(i) Reducing waste –
One of the main reasons behind implementing Six Sigma in businesses is that this methodology focuses on the manufacturing of more products by using very few inputs like time, space, effort, resources, and energy. In that way, it also reduces wasteful business activities which do not add value to the process.
We know that time delay and high operational costs, also variation in the process, or defect generation in the process are the main sources of waste in any business so this methodology works on reducing these sources with the help of different quality tools.
Managing waste is an important aspect of any business so doing this Six Sigma methodology makes processes effective and organization profitable.
(ii) Increase customer loyalty –
Customer loyalty is nothing but the measure of a customer’s likeliness to do repeat business with a company or brand. It is the result of customer satisfaction, positive customer experiences, and the overall value of goods or services the customer receives from the company.
This Six Sigma methodology has proven to be necessary for achieving the ultimate goal of increasing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
The implementation of Six Sigma processes and policies encourages management to employ any customer feedback or complaints while continually treating the quality defects until the customer is satisfied.
It focuses on solving customers’ problems continuously and making them satisfied with the best service hence it will automatically increase customer loyalty.
(iii) Improve productivity at the workplace –
“Time is money” this quote is important in our personal as well as professional lives. Managing time is of utmost importance in today’s competitive world, similarly for business also time management plays a crucial role because every minute counts and represents money, either earned or wasted.
While applying Six Sigma principles, employees are required to present a set of goals that they strive to achieve. Six Sigma implementation has proven to help employees better manage their time and this usually results in increased business productivity.
(iv) Boost employee motivation –
Motivation is one of the most important aspects for individuals as well as for big corporations. We know that the goal of every business is to have qualified and efficient staff. Naturally, motivated employees tend to be more efficient when compared to the ones who lack motivation.
Many companies have increased their worker’s productivity by as much as 50% only by fully engaging their employee. With Six Sigma tools, the organization can create a system that will motivate the employee to conduct the assigned duties at the workplace.
(V) High revenue and lower cost –
In today’s world, every company wants to become highly profitable, and the best way to achieve this is through Six Sigma implementation. Successful implementation of this methodology increases the profit and market share of a company.
For many organizations, increasing the amount of profits generated is crucial as that enables their survival in highly competitive markets.
Six Sigma requires business owners to take a deeper look into their processes and make wise decisions before undertaking any concrete action.
These decisions are fact-based and lead to improved quality and profit maximization. The more qualitative your products and services are, the more money your business will generate.
Thus Six Sigma will identify the most problematic and complex aspects of your business and guide you toward taking proper steps in solving them.
By consistently doing this, will improve performance and get your business closer and closer to operational excellence.
Application of Six Sigma methodology –
This powerful methodology is successfully used across big organizations like Motorola, and GE as well as in mid-size or small organizations.
After its first application at Motorola in the late 1980s, other international organizations also recorded a high number of savings after applying Six Sigma.
Johnson and Johnson with $600 million of reported savings, Texas Instruments recorded savings of $500 million, Sony, Boeing, and Allied signal has also achieved a large percentage of waste reduction and recorded a high amount of savings. check out the Six Sigma cost and savings in different companies.
Earlier there was a myth about Six Sigma that this methodology was only useful in Manufacturing but when the construction company also implemented this successfully then this myth permanently broke down.
One big construction company Tinjin Xianyi Construction Technology Ltd found that the construction time and construction waste at the site were both reduced by a high percentage after the implementation of Six Sigma.
One of the largest construction companies in the world, Bechtel Corporation, invested $30 million in the Six Sigma program in order to identify or prevent rework/ repair activities and in the end, after successful implementation of this methodology they recorded savings of $200 million. These examples change the way people look at this powerful technique.
In the healthcare industry also Six Sigma provided powerful results. Many hospitals implemented this and got the best results. Then comes the Supply chain, which is one of the most important parts of any business.
Its primary functions are products must be delivered to the right clients at the right time simultaneously preserving the products throughout the supply chain cycle.
Six Sigma helps achieve this effectively by constantly focusing on product quality and guaranteeing delivery deadlines.
In the banking sector, Six Sigma played important roles by improving the accuracy of allocation of cash to reduce bank charges and automatic payments, improving accuracy, reducing documentary credit defects, and reducing variation in collector performance.
Top financial institutions like Bank of America, American Express, Sun Trust Bank, and JP Morgan Chase reported positive improvements in their operations after the Six Sigma implementation.

Challenges of Six Sigma methodology–
Six Sigma is not without its challenges. As an expansive method that requires a commitment to continuous improvement, Six Sigma is often viewed as an expensive or unnecessary process, especially for small or mid-sized organizations.
There are some obstacles and challenges that often stand in the way of positive results from Six Sigma. let’s have a look at that.
(i) Lack of support –
Six Sigma requires support and buy-in at all levels of an organization. Leaders and executives must be willing to back initiatives with resources like financial or labor-related.
Subject matter experts must be open to sharing information about processes with project teams and employees at all levels must embrace the idea of change and improvement and active participation in training.
There are some barriers that cause a lack of support for the Six Sigma implementation like leaders are unfamiliar with or do not understand this methodology or they may lose interest in Six Sigma projects, and Workplace staff is fearful about the change.
Because they don’t want improvement, employees also resist change due to fear of Job loss, department heads not co-operate well with the project team.
(ii) Lack of resources or knowledge –
This can be a challenge to Six Sigma implementation, lack of knowledge about how to use and implement Six Sigma is one of the first issues small and mid-sized companies face. A small business can’t always afford to hire dedicated resources to handle continuous process improvement.
However the availability of resources and Six Sigma training makes it increasingly possible for companies to use some of the tools without an expert or to send in-house staff to be certified in Six Sigma.
(iii) Misconception about using Six Sigma in a specific industry-
This methodology originated in the manufacturing industry (Motorola) as we see in the 1st paragraph of this article. Many concepts and tools of the methodology are still taught in the context of a factory or industrial environment.
Because of this, companies often believe it will be too difficult to implement in other industries but in reality, this can be implemented in any industry.
(iv) Data access issue –
Data and analytics issues are common for organizations of all sizes. Gaining access to consistent and accurate data streams and applying statistical analysis to that data in an accurate manner is difficult. The data-related challenges are given below –
- Industry compliance rules make it difficult to gain access to necessary data.
- Take too much time between raw data capturing and access.
- The use of manual data processes in many processes.
- Discovering that an important process metric is not being captured.
(v) Poor project execution –
Companies implement Six Sigma for the first time and if they get failed then they get away from this methodology or improvement culture. Poor project execution makes it difficult for companies to adopt this methodology for the second time.
Teams can help avoid poor project performance by taking extreme care to execute every phase of the project correctly and by choosing low risks and high-reward improvements teams can also achieve success the first time.
Conclusion –
I think we discussed everything about Six Sigma starting from its history, the definition from different perspectives, principles, benefits, and challenges in its implementation, even if you are totally new to this field I am sure now you have a basic idea about what is Six Sigma and how useful it is.
This is just the beginning of this powerful methodology, there are so many things to learn. If you want to learn more then check out the other articles and get certified in Six Sigma with EALSS Academy.
If you found this article useful then please share it with your network and subscribe to get more such articles every week.






Pingback: What is Green belt Six Sigma certification?
Pingback: What is the 7 qc tools for process improvement?
Pingback: What is Six Sigma VOC (Voice of Customer)?
Pingback: Top 5 techniques for group decision making in Six Sigma
Pingback: How Root Cause Analysis can help you solve complex problems?
Pingback: How to create Project charter in Six Sigma project?
Pingback: Kaizen Tools: 5 Tools You Must Know for Continuous Improvement
Pingback: Explain Total Quality Management and Its 8 Key Principles
Pingback: How 5W2H Method Can Be Used for Problem Solving?
Pingback: FMEA: How To Perform Failure Mode Effect Analysis?
Pingback: 4 Types of Data You Must Know For Process Improvement Projects
Pingback: Histogram Vs Bar Graph: The 8 Key Differences Between Both
Pingback: Scatter Diagram: How To Utilize It For Data Analysis?