We know that if an organization wants to become a Six Sigma organization either they use the DMAIC process cycle or the DMADV Cycle. These two are popular process improvement methods used by all the top companies to improve their processes and implementation of this results in a more streamlined process with less waste and more consistent products with fewer defects.
Most of the manufacturing industries and also service-based industries use the DMAIC process cycle to implement Lean Six Sigma programs at their workplace.
DMAIC is a structured, customer-focused, and data-driven methodology for problem-solving. In this article, I am going to discuss the DMAIC methodology in detail with one example. So let’s start…
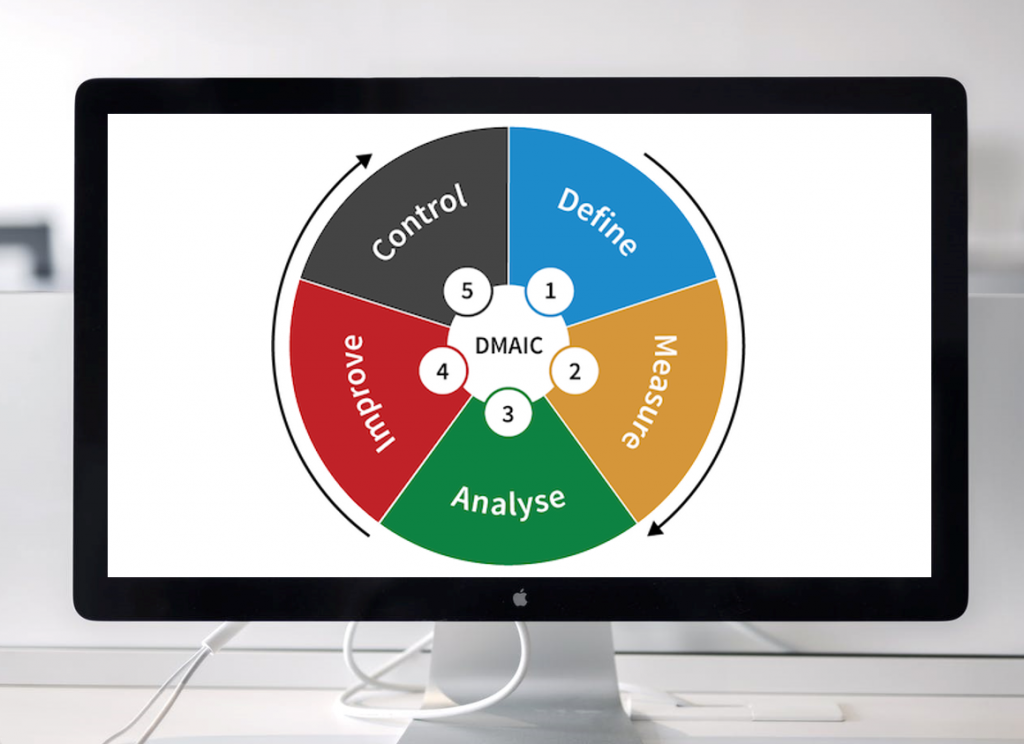
DMAIC meaning –
DMAIC Six Sigma is a data-driven process improvement methodology used to improve, optimize and stabilize business processes.
The focus of this problem-solving technique is to identify issues in the process like defects or variation and then work on solving those issues to improve the process performance and get quality outcomes or results.
This methodology is an integral part of the Six Sigma program (Understand Six Sigma in detail) and is applicable in manufacturing as well as in the services industry to improve an existing process. DMAIC process is broken into five phases: DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control, etc.
Each phase has a specific purpose and specific tools or techniques which aid in achieving the phase objectives as well as lead six sigma professionals to a significant conclusion.
The main activities of the DMAIC project include identifying the critical inputs or causes (the X’s) that are creating the problem(the Y), verifying those causes, brainstorming and selecting solutions, implementing solutions, and creating a control plan to ensure the improvement state is maintained. We will discuss these phases in detail later in this article.
Read more – What is Six Sigma methodology?
Get certified in Lean Six Sigma – EALSS Academy
When to use the DMAIC process?
We know that DMAIC and DMADV are methodologies of the Six Sigma program. Both these methods are used in different situations because DMAIC can’t be applicable in all situations same is the case with DMADV, that’s why it is important that we need to understand when to use which methodology to perform an improvement project.
There are some specific conditions where we can use DMAIC for improvement so recognizing those conditions and selecting the right problem to solve are the best way to use DMAIC. Six Sigma DMAIC approach can be used for incremental improvement. There are a few criteria on the basis of which we decide whether to use DMAIC or not? let’s see below:
- If there are defects or variations in the existing process.
- If the existing process requires improvements to meet business goals and customer satisfaction.
- If the root cause of the process problem is not known.
- If the solution to the problem is not known.
- The process we want to improve has to be tied to business results and strategic goals.
- If resolving problems and improving process performance has been the top priority for business leaders.
We need to check these criteria before applying the DMAIC model. In these situations, DMAIC provides a structured data-driven approach to truly create improvements.
DMAIC Process Phases –
As we know DMAIC process follows 5 phases and completing each phase leads to the completion of the improvement project. (DMAIC full form define, measure, analyze, improve, control) Let’s understand each phase one by one.
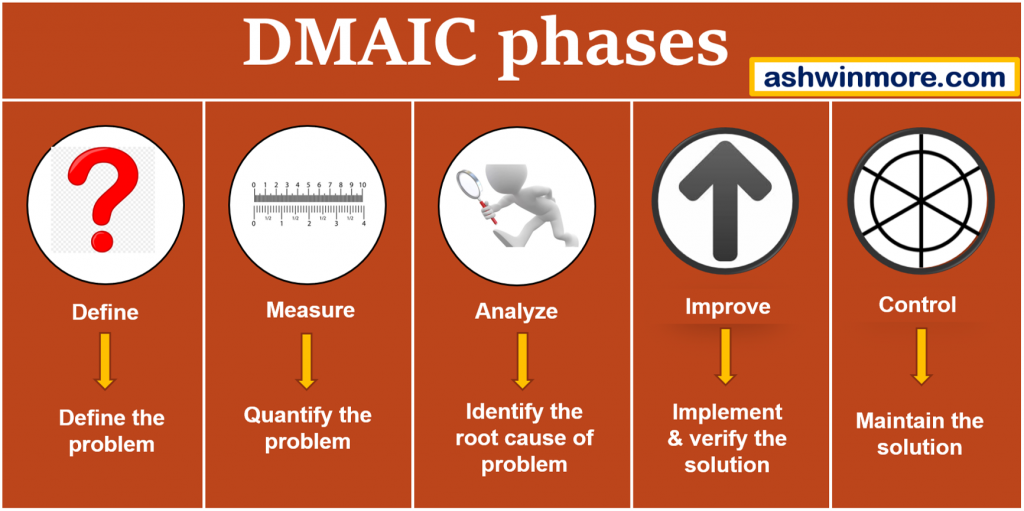
Define phase –
DMAIC define phase is the 1st phase of the Six Sigma improvement project. During this phase, initially, the team will create the project charter and basic plan for work.
A charter is a complete summary of the project. It provides complete some common information and a summary of what the team hopes to accomplish.
The charter usually features a list of team members, names of those responsible for outcomes, a problem statement, a goal, and some basic definitions of scope and metrics for success also the rough timeline estimate for the project.
During the Six Sigma define phase, the team creates a list of measurable customer requirements and creates high-level documents about the process like a process map.
Generally, the team will start with a SIPOC diagram to help them begin to understand a process. Teams should also identify stakeholders, who are individuals both within and without an organization, who have some level of influence on the success of a DMAIC project.
By understanding who stakeholders are, teams can remain in contact with various persons throughout the project, communicating with all those stakeholders as needed to ensure the future viability of improvement that is created. The goal of the Define phase is to establish the project foundation by defining the actual problem in the process.
Various tools used in the Define phase-
- Business case
- Project charter
- High-level process map
- SIPOC diagram
- Stakeholder analysis
- Tree diagram for customer needs. (VOC to CTQ conversion)
- Pareto charts.
- Value stream map.
Measure phase –
DMAIC measure phase is 2nd important phase of the project. During the measure phase team is concerned with creating a baseline metric for the process and refining problem statements and other output of the define stage.
Creating a baseline metric lets the team understand how a process should be measured and how the process is really performing before the improvement begin.
Most of the measure phase is occupied with actually gathering data (possible X’s) and formatting it in a way that can be analyzed. This is one of the difficult tasks of the six sigma project.
It requires strong observation skills, an understanding of the reasons behind the measure, knowledge of data types such as discrete and continuous, tools for measurement, and strong knowledge of statistical analysis.
The project team needs to understand the processes in as much detail as possible, creating a measured, detailed process map this is carefully reviewed in order to identify inputs in the process which are likely to influence the output (Y) or CTQ parameters.
A data collection plan will be developed and then measurement system analysis should be performed to make sure that the data we collect is correct.
After the validation of data, process stability is checked and the capability analysis is performed to check the current performance of the process. These data collection and measurements will help the team to define performance requirements for new (after improvement) processes.
Measure phase is the most challenging phase for the six sigma leader because it is completely focused on the collection of data with accuracy and precision. Various tools used in this phase-
- Process maps like linear maps, VSM, and swim lane maps.
- Cause and effect diagram
- Failure mode effect analysis(FMEA)
- XY matrix.
- Data collection plan.
- Six sigma statistics.
- Descriptive statistics and normal distribution.
- Graphical analysis like BOX-plot, Histogram, time series plot, etc.
- Measurement system analysis
- Variable/continuous gauge R & R study.
- Process capability study.
Analyze phase-
In DMAIC analyze phase, teams perform detective work on the process. Using the clues gathered during the define phase and measure phases, along with information provided by the sponsor, process owner, and subject matter experts, teams attempt to identify root causes for a problem.
The team develops hypotheses about causal relationships between inputs and outputs i.e between X’s and Y, they narrow causation down to the vital few variables and they use statistical analysis and data to validate the hypotheses and assumptions they have made in earlier phases.
The main objective of this phase is to establish the transfer function of Y= f(x) and validate a list of critical X’s and their impacts on output (Y).
During this phase, the team also starts preparing for improve phase. Teams might begin working on possible solutions and selecting solutions, developing improvement plans, and preparing documentation about improvement work.
As we saw, in the define phase team use tools like process mapping to identify all possible X’s, and then in the measure phase, they use tools like FMEA, XY matrix to refine possible X’s and at this phase team ‘disassemble’ the data to determine what it tells about the process. Various tools used in this phase-
- Pareto charts.
- Cause and effect diagram.
- Brainstorming.
- 5 why analysis.
- Hypothesis testing.
- Correlation analysis and scatter plot.
- Regression analysis.
Improve phase-
The DMAIC improve phase is aimed only at making the improvements like improving the designing, testing, and implementing of the solution.
Six Sigma team selects a final solution and begins to put it in place but sometimes they select more than one solution then it becomes difficult to determine which solution actually improves the process.
In such cases, they use a tool called improvement solution selection matrix, or they implement one change at a time and verify how it affects the process.
While selecting the solution, teams must keep the project definition in mind. The solution must address a root cause verified in analyze phase and that root cause must be directly related to the problem stated during the define phase.
After selecting the solution, teams test them using statistical tools to ensure the effectiveness of the solution before deploying that to a live-work environment. various tools used in this phase –
- Solution selection matrix.
- Design of experiments(DOE).
- Implementation plan.
- Brainstorming.
- Affinity diagram.
- Poka-yoke.
Control phase –
DMAIC control phase is the final phase of the Six Sigma project, which establishes an automated and managed mechanism to maintain and sustain improvements in the process. During this phase, teams handle 4 tasks –
- Creating the foundation for process discipline.
- Finalizing documents regarding the improvements.
- Establish ongoing metrics to evaluate the process.
- Creating a process management plan and transferring it to the process owner.
In the end, control and standards are established so that improvements can be maintained and responsibility for those improvements is transitioned to the process owner, this team also works with the process owner to handle any problems with improvements.
For this, the team uses standardized documentation, employee training, and ongoing process monitoring with a control chart and statistical process control. various tools used in this phase –
- Standard work
- Response action plan.
- Standard operating procedures.
- Poka-yoke.
- 5S program.
- Control plan like documentation and training plan.
- Control charts and SPC.
After the end of the six sigma project, Six Sigma leaders should make it a point to recognize the work of the team members in front of the project sponsor or champion and when possible, in front of departments for which the improvement is being made. This is like a reward system for each team member for their effort during the project.
Now you got a basic idea of each phase of DMAIC and the different DMAIC tools used by six sigma teams during each phase. let’s understand how it works with one practical example.
Read more – 15 reasons to go for Lean Six Sigma certification.
DMAIC Process Example –
Let’s take a scenario, John working as a project engineer in ABC Pvt. ltd, he has just received his annual performance appraisal which was based on a 360-degree review process. John is not happy with his result because on a scale of 1 to 5 ( 5 – High, 1- Low ), he got a rating of just 2.
However, instead of complaining about the result, he decided to take the result seriously and do something about it. After thinking about this, finally, he decided to use the DMAIC model for his personal improvement.

Define –
At the define phase, he is going to understand the problem initially and then define the goal statement, so as he is unhappy with his personal performance and he wants to move his performance rating from 2 to a 4 by the next annual performance appraisal. Hence his goal is to improve his rating by 2 points i.e. from 2 to 4.
Measure –
Given performance appraisal is very detailed and that allows john to decompose his average result into various components that he can associate with a particular behavior.
So he started collecting data from that appraisal report which highlights the important causes that why he got a low-performance rating and then at the next stage he will analyze that data to understand why his rating is low? how he can improve? etc.
Analyze –
Now at this stage, he is analyzing the results of each component of performance appraisal and he also created a Pareto chart to determine which component has the greatest influence on his performance rating score.
After this, he got the top five behavior, that he needs to focus on in order to improve his performance rating score. In the next stage, he will create an action plan that will improve his most important behavior which is responsible for his low rating score in performance appraisal.
Improve –
As per his identified five behaviors, he selected the one which reduced his rating score i.e. not learning new skills and not enrolling in most of the company training.
Because of this reason, his performance rating score has been reduced. Now he decided to develop an action plan and execute it, this plan primarily focuses on taking company-sponsored training and enrolling in skill-based courses.
Control –
Whatever he learned in training and courses, he started implementing it at the workplace. He also created a journal that tracks, what he learned in training courses and how much of that he implemented or applied at the workplace.
He developed a personal feedback sheet for himself, every weekend he used to give feedback to himself whether he applied or not the learnings of the course practically.
By using that feedback sheet, He also checks whether his performance is improving or not. If everything is going well he just follows the same steps in the next week but if anything is wrong then he revisits his improvement action plan and makes appropriate changes and then starts following those changes in the next week.
That’s how John keeps himself on track of personal improvement. Finally, in the next performance appraisal, his rating score increased from 2 to 4.3 (i.e 4.3/5). That’s how he achieved his target rating score by using the DMAIC approach.
This is the most simplified example that shows how useful and easily, we can apply the DMAIC process even in our daily situations to get the best results.
Conclusion –
DMAIC process is a powerful 5 step process improvement methodology which is a key foundation of the Six Sigma methodology and is designed to create efficient processes and improve productivity. This approach is the number one choice for consultants/problem solvers to improve the overall performance of the organization.
I hope now you understood this powerful methodology. We talked about the basics of the DMAIC process like what would happen during each phase, and different DMAIC tools, we also discussed one example to understand how this methodology works.
This completes our discussion on the DMAIC process. If you found this article useful then please share it in your network and subscribe to get such knowledgeable content every week.






Pingback: All about ASQ Six Sigma black belt certification.
Pingback: How Fishbone diagram is useful to identify root causes of problem?
Pingback: Lean vs Six Sigma: What are the important differences?
Pingback: How to create Project charter in Six Sigma project?
Pingback: DMAIC vs DMADV: Which Methodology Is Right For You?
Pingback: How Root Cause Analysis can help you solve complex problems?
Pingback: What is Six Sigma VOC (Voice of Customer)?
Pingback: What is Control Plan in Quality? Complete Guide for 2024
Pingback: What is the Cost of Six Sigma certification?
Pingback: How to make Pareto chart on Excel? Complete tutorial for 2024